Management of intercostal artery pseudoaneurysm following posterior pedicle screw insertion: illustrative case
- PMID: 39869887
- PMCID: PMC11775989
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE24291
Management of intercostal artery pseudoaneurysm following posterior pedicle screw insertion: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Pedicle screw insertion in posterior spinal surgery can cause vascular injuries, including rare intercostal artery pseudoaneurysms, which are typically discovered incidentally during reimaging. Onyx embolization is an effective treatment for small artery pseudoaneurysms.
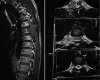
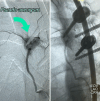
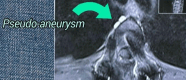
Observations: A 36-year-old man who had initially presented with back pain that remained unresponsive to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs was diagnosed with a T7-8 sarcomatous lesion confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging and biopsy. He underwent a posterior resection and T5-10 stabilization with pedicle screws. After surgery, significant hemorrhage led to his transfer for digital subtraction angiography, which revealed a prominent vascular tumor blush and a pseudoaneurysm of the right T5 intercostal artery due to screw placement. The tumor and pseudoaneurysm were effectively embolized using superselective catheterization and Onyx.
Lessons: This report highlights the dangers of intercostal artery damage from posterior spinal screws, emphasizing the need for meticulous postoperative imaging. Onyx embolization is an effective treatment for such complications. https://thejns.org/doi/10.3171/CASE24291.
Keywords: case report; intercostal artery; pedicle screw; posterior spine surgery; pseudoaneurysm.
Figures

References
-
- Boucher HH.. A method of spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959;41-B(2):248-259. - PubMed
-
- Mirza AK, Alvi MA, Naylor RM.Management of major vascular injury during pedicle screw instrumentation of thoracolumbar spine. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;163:53-59. - PubMed
-
- Giotta Lucifero A, Gragnaniello C, Baldoncini M.Rating the incidence of iatrogenic vascular injuries in thoracic and lumbar spine surgery as regards the approach: a PRISMA-based literature review. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(11):3172-3190. - PubMed
-
- Loh SA, Maldonado TS, Rockman CB.Endovascular solutions to arterial injury due to posterior spine surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55(5):1477-1481. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

