Orbital angular momentum light interacted with double quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid structure under spontaneous coherence
- PMID: 39870710
- PMCID: PMC11772622
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86417-w
Orbital angular momentum light interacted with double quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid structure under spontaneous coherence
Abstract
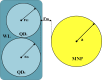
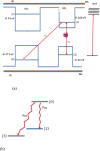
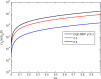
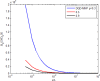
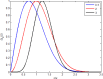
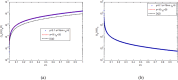
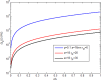
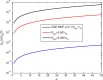
This work studies the generation of the orbital angular momentum (OAM) beam in the double quantum dot-metal nanoparticle (DQD-MNP) system under the application of the OAM beam. First, an analytical model is derived to attain the relations of probe and generated fields as a distance function in the DQD-MNP system under OAM applied field and spontaneously generated coherence (SGC) components. The calculation here is of material property; it differs from others by calculating energy states of the DQDs and the computation of the transition momenta between quantum dot (QD)-QD and QD-wetting layer (WL) transitions. The orthogonalized plane wave (OPW) calculates QD-WL transitions and their momenta. The momentum calculation is essential to specify the Rabi frequency of the input field. Such characteristics are not used in earlier models. The results show that SGC is vital in increasing the generated field. The signal field generated in the DQD-MNP system doubles that from the DQD system alone. So, the DQD-MNP system is preferred to the DQD system. The generated field in the DQD-MNP for the strong coupling DQD-MNP system is higher than that for the weak coupling. Increasing the distance separating the DQD-MNP reduces the generated field. Higher OAM number reduce the generated field at a long distance in the device. The model is then extended to study the effect of incoherent pumping ([Formula: see text]) and the relations are modified to cover this part. The results show that [Formula: see text] reduces the generated field. While the results that compare the weak and strong coupling appear for the first, others compare well to the literature.
Keywords: Double quantum dot; Metal nanoparticle; Orbital angular momentum.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent to participate: All the authors consented to participate. Consent for publication: All the authors consent to publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Energy absorbed from double quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid system.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 13;12(1):21495. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25765-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36513772 Free PMC article.
-
Entanglement in ladder-plus-Y double quantum dot structure via entropy.Appl Opt. 2019 Jan 10;58(2):369-382. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.000369. Appl Opt. 2019. PMID: 30645318
-
Second-order nonlinearity in ladder-plus-Y configuration in double quantum dot structure.Appl Opt. 2016 Dec 1;55(34):9866-9874. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.009866. Appl Opt. 2016. PMID: 27958482
-
Fano Effect and Quantum Entanglement in Hybrid Semiconductor Quantum Dot-Metal Nanoparticle System.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Jun 20;17(6):1445. doi: 10.3390/s17061445. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28632165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orbital angular momentum of photons and the entanglement of Laguerre-Gaussian modes.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017 Feb 28;375(2087):20150442. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0442. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017. PMID: 28069773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moretti, D., Felinto, D. & Tabosa, J. W. R. Collapses and revivals of stored orbital angular momentum of light in a cold-atom ensemble. Phys. Rev. A79, 023825 (2009).
-
- Hamedi, H., Reza, Ruseckas, J., Paspalakis, E. & Juzeliunas, G. Transfer of optical vortices in coherently prepared media. Phys. Rev. A99, 033812 (2019).
-
- Wang, T., Zhao, L., Jiang, L. & Yelin, S. F. Diffusion-induced decoherence of stored optical vortices. Phys. Rev. A77, 043815 (2008).
-
- Hamedi, H., Reza, Ruseckas, J. & Juzeliunas, G. Exchange of optical vortices using an electromagnetically-induced-transparency–based four-wave-mixing setup. Phys. Rev. A98, 013840 (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

