Alleviating symptoms of paediatric acute rhinosinusitis and acute otitis media with otorrhea using nasal-spraying Bacillus probiotics: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39870748
- PMCID: PMC11772584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-87372-2
Alleviating symptoms of paediatric acute rhinosinusitis and acute otitis media with otorrhea using nasal-spraying Bacillus probiotics: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
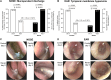
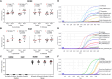
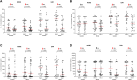
Acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) in children may be accompanied by acute otitis media (AOM) which is often associated with bacterial co-infections. These conditions are among the primary reasons that children visit hospitals and require antibiotic treatment. This study evaluated the efficacy of the nasal-spraying probiotics (LiveSpo Navax containing 5 billion Bacillus subtilis and B. clausii spores/5 mL) as a supportive treatment for dual ARS and AOM with otorrhea in a randomized, single-blind, controlled clinical trial. Eighty-two patients (41 per group), aged 1 month to 12 years, received standard care along with nasal spraying of either physiological saline (Control group) or LiveSpo Navax (Navax group), administered three times daily over a 7-day follow-up period. A total of sixty-one patients (30-31 per group) completed the trial. The Navax group experienced 68.00% and 96.77% reductions in nasal congestion (by day 3) and rhinorrhea (by day 7), respectively, which were 2.04 and 1.94-fold higher than the Control group, with odds ratios (OR) of 4.31 and 30.00 (p < 0.05). Endoscopic results indicated 8% and 11% higher reductions in nasal mucopurulent discharge and tympanic membrane hyperemia in the Navax group compared to the Control group. By day 3, compared to day 0, the Navax group exhibited > 1200-fold reduction in Streptococcus pneumoniae and ≥ 4-fold reduction in Haemophilus influenzae concentrations (p < 0.05) in both nasopharyngeal and middle ear fluid samples, whereas the Control group showed no significant reductions. Navax treatment reduced IL-6 by 1.35- to 1.74-fold and TNF-α by 1.17- to 1.45-fold, more effectively than the Control group (p < 0.05). These results suggest that nasal-spray Bacillus spore probiotics, with their ability to reduce bacterial load and modulate immune responses, provide a cost-effective and safe solution for alleviating symptoms of both ARS and AOM in children.Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier NCT05804123 on April 7, 2023.
Keywords: Acute; Bacterial co-infection; Cytokine; Nasal-spraying Bacillus spores; Otitis media; Rhinosinusitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: LiveSpo Navax is produced by LiveSpo Pharma Ltd., of which A.H.N. is the founder and scientific director. A.T.V.N. serves as a scientific consultant for LiveSpo Pharma Ltd., while both A.T.V.N. and D.P.L. are affiliated with the funder, ANABIO R&D Ltd. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The study was conducted under the supervision of VietStar Biomedical Research, a licenced Contract Research Organization by the Vietnam Ministry of Health, to ensure the objectivity and independence of the research.
Figures


References
-
- Rettig, E. M. & Tunkel, D. E. In Infections of the Ears, Nose, Throat, and Sinuses (eds Durand, M. L. & Deschler, D. G.) 45–55 (Springer, 2018).
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet386, 743–800. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

