Multimodal machine learning enables AI chatbot to diagnose ophthalmic diseases and provide high-quality medical responses
- PMID: 39870855
- PMCID: PMC11772878
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01461-0
Multimodal machine learning enables AI chatbot to diagnose ophthalmic diseases and provide high-quality medical responses
Abstract
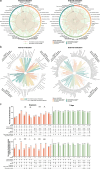
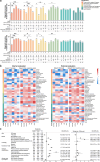
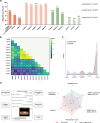
Chatbot-based multimodal AI holds promise for collecting medical histories and diagnosing ophthalmic diseases using textual and imaging data. This study developed and evaluated the ChatGPT-powered Intelligent Ophthalmic Multimodal Interactive Diagnostic System (IOMIDS) to enable patient self-diagnosis and self-triage. IOMIDS included a text model and three multimodal models (text + slit-lamp, text + smartphone, text + slit-lamp + smartphone). The performance was evaluated through a two-stage cross-sectional study across three medical centers involving 10 subspecialties and 50 diseases. Using 15640 data entries, IOMIDS actively collected and analyzed medical history alongside slit-lamp and/or smartphone images. The text + smartphone model showed the highest diagnostic accuracy (internal: 79.6%, external: 81.1%), while other multimodal models underperformed or matched the text model (internal: 69.6%, external: 72.5%). Moreover, triage accuracy was consistent across models. Multimodal approaches enhanced response quality and reduced misinformation. This proof-of-concept study highlights the potential of chatbot-based multimodal AI for self-diagnosis and self-triage. (The clinical trial was registered on June 26, 2023, on ClinicalTrials.gov under the registration number NCT05930444.).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Poon H. Multimodal generative AI for precision health. NEJM AIhttps://ai.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/AI-S2300233 (2023). - DOI
-
- Tan, T. F. et al. Artificial intelligence and digital health in global eye health: opportunities and challenges. Lancet Glob. Health11, 1432–1443 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Xu, P. S., Chen, X. L., Zhao, Z. W. & Shi, D. L. Unveiling the clinical incapabilities: a benchmarking study of GPT-4V(ision) for ophthalmic multimodal image analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol.108, 1384–1389 (2024). - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
- SHDC2023CRD013/Shanghai Hospital Development Center (SHDC)
- 82371101/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 62371326/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 62371328/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 62271337/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- U20A20170/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- BK20231310/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
- BK20211308/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

