Gender differences in oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb) changes during drawing interactions in romantic couples: an fNIRS study
- PMID: 39872040
- PMCID: PMC11769947
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1476535
Gender differences in oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb) changes during drawing interactions in romantic couples: an fNIRS study
Abstract
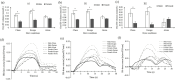
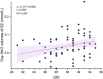
Interpersonal interaction is essential to romantic couples. Understanding how gender impacts an individual's brain activities during intimate interaction is crucial. The present study examined gender differences in oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb) changes during real-time drawing interactions between members of romantic couples using non-invasive functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). We analyzed the oxy-Hb concentrations of romantic couples engaged in interactive (i.e., chase and escape) and non-interactive (i.e., individual) drawing sessions. Our findings indicated that males (vs. females) exhibited more pronounced oxy-Hb concentrations in Broca's area, motor area, sensorimotor cortex, and temporal lobe areas than women in an interactive drawing task, suggesting a heightened goal-oriented engagement in social interaction. Significant positive correlations were found between oxy-Hb volumes of the temporal area and the Quality of Relationship Index (QRI), underscoring the impact of interpersonal dynamics on brain function during interactive tasks. This study deepens the understanding of gender differences in neural mechanisms in social interaction tasks and provides important insights for intimacy research.
Keywords: drawing interactions; fNIRS; male–female couples; oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb); real-time.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Bai, Chen, Cui and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bartlett K. A., Camba J. D. (2023). Gender differences in spatial ability: a critical review. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 35:8. doi: 10.1007/s10648-023-09728-2 - DOI
-
- Behrendt H. F., Konrad K., Perdue K. L., Firk C. (2020). Infant brain responses to live face-to-face interaction with their mothers: combining functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fnirs) with a modified still-face paradigm. Infant Behav. Dev. 58:101410. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2019.101410, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

