The optimised model of predicting protein-metal ion ligand binding residues
- PMID: 39873344
- PMCID: PMC11773433
- DOI: 10.1049/syb2.70001
The optimised model of predicting protein-metal ion ligand binding residues
Abstract
Metal ions are significant ligands that bind to proteins and play crucial roles in cell metabolism, material transport, and signal transduction. Predicting the protein-metal ion ligand binding residues (PMILBRs) accurately is a challenging task in theoretical calculations. In this study, the authors employed fused amino acids and their derived information as feature parameters to predict PMILBRs using three classical machine learning algorithms, yielding favourable prediction results. Subsequently, deep learning algorithm was incorporated in the prediction, resulting in improved results for the sets of Ca2+ and Mg2+ compared to previous studies. The validation matrix provided the optimal prediction model for each ionic ligand binding residue, exhibiting the capability of effectively predicting the binding sites of metal ion ligands for real protein chains.
Keywords: biocomputers; bioinformatics.
© 2025 The Author(s). IET Systems Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
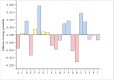


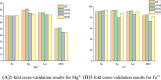

References
-
- Reed, G.H. , Poyner, R.R. : Mn2+ as a probe of divalent metal ion binding and function in enzymes and other proteins. Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 37(12), 183–207 (2000) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

