8-OHdG and Nrf2 Protein are Expressed Consistently in Various T Stages of Invasive Breast Carcinoma
- PMID: 39874013
- PMCID: PMC12082425
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.1.301
8-OHdG and Nrf2 Protein are Expressed Consistently in Various T Stages of Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Oxidative stress prompts breast cancer cells to adapt by raising the lethal threshold and enhancing the antioxidant mechanism, thereby enabling survival and continuous proliferation that facilitates tumor progression. Nrf2 and 8-OHdG are indicative of oxidative stress activity and impact the progression of breast cancer. We aimed to analyze the expression of Nrf2 and 8-OHdG in various T stages of breast cancer in our hospital.
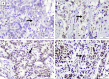
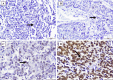
Methods: This observational study employed a cross-sectional design and included patients with invasive breast carcinoma of no special type diagnosis from histopathology examination who underwent modified radical mastectomy without neoadjuvant chemotherapy at Dr. Soetomo General Academic Hospital between January 2019 and December 2022. Medical records and paraffin blocks that met these criteria were obtained. 8-OHdG and Nrf2 were assessed using immunohistochemistry.
Result: There was no significant difference and correlation between 8-OHdG (p=0.578) and Nrf2 (p=0.694) expression with various T stages of IBC-NST and no significant correlation between 8-OHdG/Nrf2 expression and T stage (p=0.242 and 0.625 respectively).
Conclusion: Consistent expression of 8-OHdG and Nrf2 in various T stages of breast cancer represents a continuation of the oxidative stress process in breast cancer that is not influenced by the tumor size. The existence of consistent oxidative stress at all tumor sizes (T stage) stimulates breast cancer cells to continue proliferating.
Keywords: 8-OHdG; Nrf2; breast cancer; invasive breast carcinoma of no special type.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EMMPRIN Correlated with β-CATENIN in Various t Stages of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Mar 1;26(3):1001-1007. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.3.1001. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40156418 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Specialist breast care nurses for support of women with breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 3;2(2):CD005634. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005634.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559420 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic mastectomy for the prevention of breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub3. PMID: 15495033 Updated.
-
Prognostic factors for return to work in breast cancer survivors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 7;5(5):CD015124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015124.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40331515 Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, et al. Available from: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today, authors. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today [Internet] France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; c2024 [cited 2024 Aug 31]:
-
- Guo Z, Mo Z. Keap1‐Nrf2 signaling pathway in angiogenesis and vascular diseases. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(6):869–83. - PubMed
-
- Sarmiento-Salinas FL, Delgado-Magallón A, Montes-Alvarado JB, Ramírez-Ramírez D, Flores-Alonso JC, Cortés-Hernández P, et al. Breast cancer subtypes present a differential production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and susceptibility to antioxidant treatment. Front Oncol. 2019;9:480. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

