Leveraging Network Target Theory for Efficient Prediction of Drug-Disease Interactions: A Transfer Learning Approach
- PMID: 39874191
- PMCID: PMC11923905
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202409130
Leveraging Network Target Theory for Efficient Prediction of Drug-Disease Interactions: A Transfer Learning Approach
Abstract
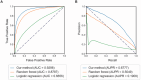
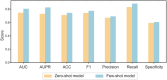
Efficient virtual screening methods can expedite drug discovery and facilitate the development of innovative therapeutics. This study presents a novel transfer learning model based on network target theory, integrating deep learning techniques with diverse biological molecular networks to predict drug-disease interactions. By incorporating network techniques that leverage vast existing knowledge, the approach enables the extraction of more precise and informative drug features, resulting in the identification of 88,161 drug-disease interactions involving 7,940 drugs and 2,986 diseases. Furthermore, this model effectively addresses the challenge of balancing large-scale positive and negative samples, leading to improved performance across various evaluation metrics such as an Area under curve (AUC) of 0.9298 and an F1 score of 0.6316. Moreover, the algorithm accurately predicts drug combinations and achieves an F1 score of 0.7746 after fine-tuning. Additionally, it identifies two previously unexplored synergistic drug combinations for distinct cancer types in disease-specific biological network environments. These findings are further validated through in vitro cytotoxicity assays, demonstrating the potential of the model to enhance drug development and identify effective treatment regimens for specific diseases.
Keywords: cancer; drug combination; drug‐disease interaction (DDIs); few‐shot learning; network target.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Drug-target interaction prediction by integrating heterogeneous information with mutual attention network.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 19;25(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05976-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39563226 Free PMC article.
-
CNN-Siam: multimodal siamese CNN-based deep learning approach for drug‒drug interaction prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 23;24(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05242-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36959539 Free PMC article.
-
Graph-DTI: A New Model for Drug-target Interaction Prediction Based on Heterogenous Network Graph Embedding.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(6):1013-1024. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230713142255. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37448360
-
Artificial intelligence to deep learning: machine intelligence approach for drug discovery.Mol Divers. 2021 Aug;25(3):1315-1360. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10217-3. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 33844136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of deep learning methods in biological networks.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Mar 22;22(2):1902-1917. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa043. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32363401 Review.
Cited by
-
A computational-based new treatment strategy with three-armed RCT on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 1;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01149-3. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40597150 Free PMC article.
-
Target identification of natural products in cancer with chemical proteomics and artificial intelligence approaches.Cancer Biol Med. 2025 Jul 9;22(6):549-97. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2025.0145. Cancer Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40631551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DiMasi J. A., Grabowski H. G., Hansen R. W., J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins A. L., Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682. - PubMed
-
- Iorio F., Knijnenburg T. A., Vis D. J., Bignell G. R., Menden M. P., Schubert M., Aben N., Gonçalves E., Barthorpe S., Lightfoot H., Cokelaer T., Greninger P., van Dyk E., Chang H., de Silva H., Heyn H., Deng X., Egan R. K., Liu Q., Mironenko T., Mitropoulos X., Richardson L., Wang J., Zhang T., Moran S., Sayols S., Soleimani M., Tamborero D., Lopez‐Bigas N., Ross‐Macdonald P., et al., Cell 2016, 166, 740. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghandi M., Huang F. W., Jané‐Valbuena J., Kryukov G. V., Lo C. C., McDonald E. R., Barretina J., Gelfand E. T., Bielski C. M., Li H., Hu K., Andreev‐Drakhlin A. Y., Kim J., Hess J. M., Haas B. J., Aguet F., Weir B. A., Rothberg M. V., Paolella B. R., Lawrence M. S., Akbani R., Lu Y., Tiv H. L., Gokhale P. C., de Weck A., Mansour A. A., Oh C., Shih J., Hadi K., Rosen Y., et al., Nature 2019, 569, 503. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
