One-Year Real-World Outcomes of Ab-Externo Gel Stent Placement From the EXPAND Study
- PMID: 39874255
- PMCID: PMC11952689
- DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000002543
One-Year Real-World Outcomes of Ab-Externo Gel Stent Placement From the EXPAND Study
Abstract
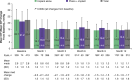
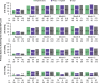
Prcis: In the real-world, retrospective, EXPAND study of consecutive adults with glaucoma, ab-externo gel stent implantation effectively lowered intraocular pressure (34%) and the medication burden (61%), with transient/self-resolving hypotony as the most frequent adverse event (28%).
Purpose: To assess effectiveness and safety of ab-externo gel stent (GS) implantation in glaucoma.
Methods: Multicenter, real-world, retrospective study. Consecutive adults with glaucoma and ab-externo GS implantation (with/without phacoemulsification or open/closed conjunctiva) ≥12 months before study entry. Data were extracted between the baseline/preoperative and last follow-up visit or date of secondary surgical intervention (SSI). Primary effectiveness endpoint: proportion of primary eyes (first eye in bilaterally implanted patients) at month 12 (M12) achieving ≥20% intraocular pressure (IOP) reduction from baseline without medication increase, clinical hypotony, vision loss to counting fingers, or SSI. Secondary effectiveness endpoints included complete success (IOP ≤18 mm Hg and ≥20% IOP reduction from medicated baseline without medication, clinical hypotony, or SSI); qualified success (same but without medication increase); and needling rate. Key safety endpoints (all eyes): intraoperative complications, postoperative adverse events (AEs), and SSIs.
Results: The safety population included 466 eyes; 80.7% received the GS alone and 85.0% were implanted with closed conjunctiva. At M12, 39.1% of all primary eyes (N=413) and 54.9% of primary eyes with IOP and medication data at baseline and M12 (N=213) achieved the primary endpoint. At M12 among all primary eyes, the complete success, qualified success, and needling rates were 33.5%, 56.5%, and 28.6%. Most eyes (97.9%) had no intraoperative complications. The most frequent postoperative AE was transient/self-resolving hypotony (IOP <6 mm Hg; 28.1%). Sixty-nine (14.8%) eyes required an SSI.
Conclusions: Ab-externo GS placement effectively lowered IOP and the medication count without unexpected complications/AEs, expanding implantation options based on patients' needs and surgeons' preferences.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Financial arrangements of the authors with companies whose products may be related to the present report are listed as declared by the authors. B.A.F. has served as a consultant for Allergan (an AbbVie company), Bausch+Lomb, BVI Endo Optiks, iStar, Ivantis, MST, and Thea, and is a speaker for Aerie Pharmaceuticals. V.V. is an employee of Allergan (an AbbVie company) and may hold AbbVie stock. J.K. has served as speaker and/or consultant/advisor for Alcon, Allergan (an AbbVie company), Bausch+Lomb, and Glaukos. M.M.B. has received research support from AbbVie, Alcon, Formosa Pharmaceutical, Glaukos, Ivantis, Novartis, and Ocular Therapeutix, and is a speaker for AbbVie and Alcon. B.L. has no disclosures to declare. D.G. has served as speaker and/or consultant/advisor to Allergan (an AbbVie company), Alcon, Johnson & Johnson, Glaukos, and New World Medical. S.V. is a consultant/advisor for Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Alcon, Allergan (an AbbVie company), Bausch+Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Glaukos, Iridex, iStar Medical, Ivantis, Sight Sciences, and Volk Optical; has received grant support from Santen, and is an equity owner of Alphaeon, Ivantis, and O3 Optix. M.B. is a current employee of Nethra Consulting LLC but was an employee of Allergan (an AbbVie company) at the time the study was conducted and may hold AbbVie stock. S.S. is a consultant for Innomar Strategies but was an employee of Allergan (an AbbVie company) at the time the study was conducted and may hold AbbVie stock. H.A. has received consulting honoraria from Allergan (an AbbVie company) and Ivantis, and research support from Allergan (an AbbVie company), Ivantis, and New World Medical. N.N.K. has received research support from Allergan (an AbbVie company), Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Diopsys, Equinox, Glaukos, Guardion Health Sciences Inc, Nicox, Olleyes, and Santen, and is a consultant to Allergan (an AbbVie company); spouse is a consultant for Alimera, Allergan (an AbbVie company), Biogen, Genentech, Iveric, Regeneron, and Vial.
Figures



References
-
- Gedde SJ, Vinod K, Wright MM, et al. . Primary open-angle glaucoma preferred practice pattern® . Ophthalmology. 2021;128:71–150. - PubMed
-
- No authors . European Glaucoma Society terminology and guidelines for glaucoma, 5th edition. Br J Ophthalmol. 2021;105(suppl 1):1–169. - PubMed
-
- Yang SA, Mitchell WG, Hall N, et al. . Usage patterns of minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) differ by glaucoma type: IRIS registry analysis 2013-2018. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2021;29:443–451. - PubMed
-
- Yang SA, Mitchell W, Hall N, et al. . Trends and usage patterns of minimally invasive glaucoma surgery in the United States: IRIS® registry analysis 2013-2018. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2021;4:558–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

