Single-cell transcriptomics of bronchoalveolar lavage during PRRSV infection with different virulence
- PMID: 39875369
- PMCID: PMC11775223
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54676-2
Single-cell transcriptomics of bronchoalveolar lavage during PRRSV infection with different virulence
Abstract
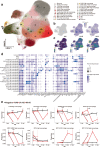
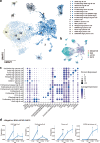
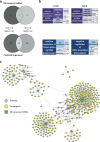
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) causes significant economic losses in the global swine industry due to its high genetic diversity and different virulence levels, which complicate disease management and vaccine development. This study evaluated longitudinal changes in the immune cell composition of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and the clinical outcomes across PRRSV strains with varying virulence, using techniques including single-cell transcriptomics. In highly virulent infection, faster viral replication results in an earlier peak lung-damage time point, marked by significant interstitial pneumonia, a significant decrease in macrophages, and an influx of lymphocytes. Viral tracking reveals less than 5% of macrophages are directly infected, and further analysis indicates bystander cell death, likely regulated by exosomal microRNAs as a significant factor. In contrast, the peak intermediate infection shows a delayed lung-damage time point with fewer cell population modifications. Furthermore, anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophages (SPP1-CXCL14high) are identified and their counts increase during the peak lung-damage time point, likely contributing to local defense and lung recovery, which is not observed in high virulent infection. These findings provide a comprehensive description of the immune cellular landscape and differential PRRSV virulence mechanisms, which will help build new hypotheses to understand PRRSV pathogenesis and other respiratory infections.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ogno, G. et al. Impact of PRRSV strains of different in vivo virulence on the macrophage population of the thymus. Vet. Microbiol.232, 137–145 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Teifke, J. et al. Detection of European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in porcine alveolar macrophages by two-colour immunofluorescence and in-situ hybridization-immunohistochemistry double labelling. J. Comp. Pathol.124, 238–245 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Lunney, J. K. et al. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci.4, 129–154 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

