Robust mucosal SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells effectively combat COVID-19 and establish polyfunctional resident memory in patient lungs
- PMID: 39875584
- PMCID: PMC11876067
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-02072-9
Robust mucosal SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells effectively combat COVID-19 and establish polyfunctional resident memory in patient lungs
Abstract
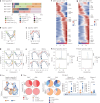
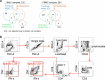
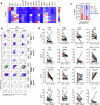
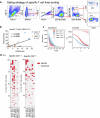
Mucosal antigen-specific T cells are pivotal for pathogen clearance and immune modulation in respiratory infections. Dysregulated T cell responses exacerbate coronavirus disease 2019 severity, marked by cytokine storms and respiratory failure. Despite extensive description in peripheral blood, the characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-specific T cells in the lungs remain elusive. Here we conducted integrated single-cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in 122 bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and 280 blood samples from 159 patients, including 27 paired BALF and blood samples from 24 patients. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells were robustly elicited in BALF irrespective of prior vaccination, correlating with diminished viral loads, lessened systemic inflammation and improved respiratory function. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in BALF exhibited profound activation, along with proliferative and multi-cytokine-producing capabilities and a glycolysis-driven metabolic signature, which were distinct from those observed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. After viral clearance, these specific T cells maintained a polyfunctional tissue-resident memory phenotype, highlighting their critical roles in infection control and long-term protection.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Roukens, A. H. E. et al. Prolonged activation of nasal immune cell populations and development of tissue-resident SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cell responses following COVID-19. Nat. Immunol.23, 23–32 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

