Modeling Sporadic Progressive Supranuclear Palsy in 3D Midbrain Organoids: Recapitulating Disease Features for In Vitro Diagnosis and Drug Discovery
- PMID: 39876539
- PMCID: PMC12010066
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.27172
Modeling Sporadic Progressive Supranuclear Palsy in 3D Midbrain Organoids: Recapitulating Disease Features for In Vitro Diagnosis and Drug Discovery
Abstract
Objective: Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) is a severe neurodegenerative disease characterized by tangles of hyperphosphorylated tau protein and tufted astrocytes. Developing treatments for PSP is challenging due to the lack of disease models reproducing its key pathological features. This study aimed to model sporadic PSP-Richardson's syndrome (PSP-RS) using multi-donor midbrain organoids (MOs).
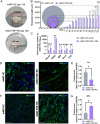
Methods: The MOs were generated by pooling induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from 4 patients with sporadic probable PSP-RS and compared them with MOs from 3 healthy control (HC) subjects. We performed comprehensive analyses of MOs over 120 days to assess neuronal death, reactive gliosis, and the accumulation of 4R-tau and hyperphosphorylated tau forms (pThr231, pSer396, pThr181, and pSer202/pThr205 [AT8]) using immunofluorescence microscopy and Western blot. On day 90, immunohistochemical analysis using pSer396 and AT8 antibodies was conducted to assess disease pathology.
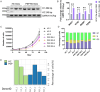
Results: PSP-derived MOs showed progressive size reduction compared with HC-derived MOs, linked to upregulated apoptosis-related mRNA markers. Dopaminergic neuron degeneration was marked by decreased tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and increased neurofilament light chain (NfL). Immunofluorescence and Western blot revealed accumulation of all investigated tau forms with a peak at 90 days, along with a significant rise in GFAP-positive cells in PSP-derived MOs. Immunochemistry confirmed typical PSP histological alterations, such as neurofibrillary tangles and tufted-shaped astrocytes, absent in HC-derived organoids.
Interpretation: We developed a robust in vitro PSP model reproducing the key molecular and histologic features of the disease. This result holds promise for advancing basic and clinical research in PSP, paving the way for in vitro molecular diagnosis and identification of novel therapeutic targets. ANN NEUROL 2025;97:845-859.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PNRR (PIANO NAZIONALE DI RIPRESA E RESILIENZA) National Center for Gene Therapy and Drugs based on RNA technology. A multiscale integrated approach to the study of the nervous system in health and disease (MNESYS). Advanced iPSC-based model of human drug-resistant mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) linked to SCN1A mutations (2022J2ARST)
- 20240532/The Carfoord Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

