Changes of b2-microglobulin and electrolytes in different stages of COPD and their value in evaluating prognosis
- PMID: 39876906
- PMCID: PMC11771965
- DOI: 10.5937/jomb0-50905
Changes of b2-microglobulin and electrolytes in different stages of COPD and their value in evaluating prognosis
Abstract
Background: To investigate the changes of b2-microglobulin and electrolyte in different stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and the value of evaluating prognosis.
Methods: A retrospective study was undertaken on 120 patients diagnosed with COPD and treated at our respiratory department between February 1, 2020, and January 31, 2023. These patients were classified into three groups based on the GOLD classification: mild (FEV1 > 81%), moderate (51% < FEV1 ≤ 80%), and severe (FEV1 ≤ 50%). As a control group, 40 healthy individuals who had routine examinations during the same period were selected. The COPD patients were then followed up and divided into a good prognosis group (n = 67) and a poor prognosis group (n = 53). The levels of b2-microglobulin and electrolytes were measured in patients with different stages of the disease and different prognoses. Kendall's tau-b and ordered logistic regression were employed to analyze how the changes in b2-microglobulin and electrolyte levels correlated with disease severity. Furthermore, the prognostic value of b2-microglobulin and electrolyte levels in COPD was assessed using an ROC curve.
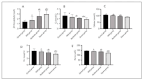
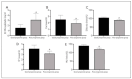
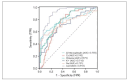
Results: In comparison to the control group, the severity of COPD patients displayed a notable increase in b2microglobulin levels, while there was a significant decrease in levels of calcium, chlorine, potassium, and sodium. Kendall's tau-b correlation coefficient analysis indicated a positive correlation between COPD severity and b2microglobulin, and a negative correlation between COPD severity and levels of calcium, chlorine, potassium, and sodium. Logistic regression analysis revealed that there was a positive correlation between disease severity and b2microglobulin, and a negative correlation between disease severity and levels of calcium, chlorine, potassium, and sodium. Furthermore, the poor prognosis group exhibited a significant increase in b2-microglobulin levels, alongside a significant decrease in levels of calcium, chlorine, potassium, and sodium compared to the good prognosis group (P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis demonstrated that a combined detection of b2-microglobulin, calcium, chlorine, potassium, and sodium yielded significantly higher area under the curve, sensitivity, and specificity values compared to single detection methods, highlighting its significant predictive value for COPD prognosis.
Conclusions: Patients who presented with a more severe form of the disease exhibited elevated levels of b2microglobulin and reduced electrolyte levels. Prognostic accuracy was significantly enhanced when b2-microglobulin and electrolyte levels were analyzed together, offering a superior method for predicting patient outcomes.
Uvod: Cilj je bio da se ispitaju promene b2-mikroglobulina i elektrolita u različitim stadijumima hronične opstruktivne plućne bolesti (HOBP) i vrednosti procene prognoze.
Metode: Retrospektivna studija je sprovedena na 120 pacijenata sa dijagnozom HOBP i lečenih na našem respiratornom odeljenju u periodu od 1. februara 2020. do 31. januara 2023. Ovi pacijenti su klasifikovani u tri grupe na osnovu GOLD klasifikacije: blagi (FEV1 > 81%), umereno (51% < FEV1 ≤ 80%) i teško (FEV1 ≤ 50%). Kao kontrolnu grupu odabrano je 40 zdravih osoba koje su u istom periodu bile na rutinskim pregledima. Pacijenti sa HOBP su zatim praćeni i podeljeni u grupu sa dobrom prognozom (n = 67) i grupu sa lošom prognozom (n = 53). Nivoi b2-mikroglobulina i elektrolita su mereni kod pacijenata sa različitim stadijumima bolesti i različitim prognozama. Kendallova tau-b i naređena logistička regresija su korišćeni da se analizira kako su promene u b2-mikroglobulinu i nivoima elektrolita u korelaciji sa ozbiljnošću bolesti. Štaviše, prognostička vrednost b2-mikroglobulina i nivoa elektrolita u HOBP je procenjena korišćenjem ROC krive.
Rezultati: U poređenju sa kontrolnom grupom, težina bolesnika sa HOBP pokazala je značajno povećanje nivoa b2-mikroglobulina, dok je došlo do značajnog smanjenja nivoa kalcijuma, hlora, kalijuma i natrijuma. Kendallova analiza koeficijenta tau-b korelacije pokazala je pozitivnu korelaciju između težine HOBP i b2-mikroglobulina, i negativnu korelaciju između težine HOBP i nivoa kalcijuma, hlora, kalijuma i natrijuma. Logistička regresiona analiza je otkrila da postoji pozitivna korelacija između težine bolesti i b2-mikroglobulina i negativna korelacija između težine bolesti i nivoa kalcijuma, hlora, kalijuma i natrijuma. Pored toga, grupa sa lošom prognozom pokazala je značajno povećanje nivoa b2-mikroglobulina, uz značajno smanjenje nivoa kalcijuma, hlora, kalijuma i natrijuma u poređenju sa grupom sa dobrom prognozom (P <0,05). Analiza ROC krive je pokazala da je kombinovana detekcija b2-mikroglobulina, kalcijuma, hlora, kalijuma i natrijuma dala značajno veću površinu ispod krive, osetljivost i vrednosti specifičnosti u poređenju sa pojedinačnim metodama detekcije, naglašavajući njegovu značajnu prediktivnu vrednost za prognozu HOBP.
Zaključak: Pacijenti koji su imali teži oblik bolesti su ispoljili povišen nivo b2-mikroglobulina i smanjen nivo elektrolita. Prognostička tačnost je značajno poboljšana kada su b2-mikroglobulin i nivoi elektrolita analizirani zajedno, nudeći superiorni metod za predviđanje ishoda pacijenata.
Keywords: b2-microglobulin; electrolyte; severity of COPD.
2024 Lin Wang, Rong Yi, Lanlan Wei, Jiali Xiong, published by CEON/CEES.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this work.Conflict of Interest: The authors stated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Soodaeva S, Kubysheva N, Klimanov I, Shutov A, Eliseeva T, Novikov V, et al The differences in the levels of oxidative status marker and soluble CD95 in patients with moderate to severe COPD during an exacerbation and a stable period. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:2105406. doi: 10.1155/2021/2105406. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sahin H, Naz I, Susam S, Erbaycu A E, Olcay S. The effect of the presence and severity of bronchiectasis on the respiratory functions, exercise capacity, dyspnea perception, and quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Thorac Med. 2020;15(1):26. doi: 10.4103/atm.atm_198_19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jin Y X, Zhang S, Xiao J, Wang Z H, Dong C, You L L, et al Association between serum beta(2)-microglobulin levels and the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in Chinese patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Bmc Nephrol. 2023;24(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03191-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
