The Effectiveness of Surgical Thrombectomy via Below-Knee Popliteal Artery for the Treatment of Acute Limb Ischemia
- PMID: 39877322
- PMCID: PMC11774520
- DOI: 10.3400/avd.oa.24-00115
The Effectiveness of Surgical Thrombectomy via Below-Knee Popliteal Artery for the Treatment of Acute Limb Ischemia
Abstract
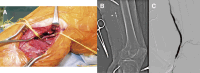
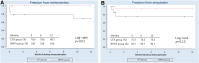
Objectives: Surgical thrombectomy has been established as an effective treatment for acute limb ischemia (ALI). Nevertheless, manipulation via the common femoral artery (CFA) to retrieve thrombus in the infra-popliteal artery sometimes proves less effective. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed patients undergoing surgical thrombectomy for infra-inguinal ALI from January 2010 to December 2022. The primary endpoint was the rate of amputation. Secondary endpoints were technical and clinical success rates, incidence of distal embolism, and freedom from reintervention. Results: A total of 35 patients underwent surgical thrombectomy where the popliteal artery or below is occluded. The CFA approach was utilized in 13, and the below-knee popliteal artery (BKPA) approach in 22. There were no differences in background between groups. The reintervention rate was lower in the BKPA group (BKPA group: 0% vs. CFA group: 30.8%; P = 0.01). The BKPA group showed a significantly lower incidence of distal embolism (BKPA group: 4.5% vs. CFA group: 38.5%; P = 0.02) and freedom from reintervention (BKPA group 100% at 12 months vs. CFA group: 68.7% at 12 months; log-rank P = 0.01). Conclusions: The BKPA approach-first strategy for surgical thrombectomy in the management of ALI is feasible with better outcomes compared with the CFA approach.
Keywords: acute limb ischemia; below-knee popliteal artery; surgical revascularization; thrombectomy.
© 2025 The Editorial Committee of Annals of Vascular Diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-term outcomes of endovascular management of acute limb ischemia using aspiration mechanical thrombectomy.Vascular. 2025 Feb;33(1):34-41. doi: 10.1177/17085381241236923. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Vascular. 2025. PMID: 38415647
-
Importance of Successful Revascularization in Acute Limb Ischemia: Sub-Analysis From the RESCUE ALI Trial.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Jan;105(1):211-218. doi: 10.1002/ccd.31319. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025. PMID: 39627985 Free PMC article.
-
Vein bypass first vs. best endovascular treatment first revascularisation strategy for chronic limb-threatening ischaemia due to infra-popliteal disease: the BASIL-2 RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(65):1-72. doi: 10.3310/YTFV4524. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39397484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of combined superficial femoral artery endovascular therapy with popliteal-to-distal bypass: A paradigm shift in surgical open bypass for chronic limb-threatening ischemia.Vascular. 2021 Dec;29(6):905-912. doi: 10.1177/1708538120981224. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Vascular. 2021. PMID: 33349196
-
Popliteal artery aneurysms. Factors associated with thromboembolism and graft failure.Int Angiol. 2004 Mar;23(1):54-65. Int Angiol. 2004. PMID: 15156131 Review.
References
-
- Korabathina R, Weintraub AR, Price LL, et al. Twenty-year analysis of trends in the incidence and in-hospital mortality for lower-extremity arterial thromboembolism. Circulation 2013; 128: 115–21. - PubMed
-
- Fogarty TJ, Cranley JJ, Krause RJ, et al. A method for extraction of arterial emboli and thrombi. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1963; 116: 241–4. - PubMed
-
- Björck M, Earnshaw JJ, Acosta S, et al. Editor’s choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2020 clinical practice guidelines on the management of acute limb ischaemia. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2020; 59: 173–218. - PubMed
-
- Hess CN, Huang Z, Patel MR, et al. Acute limb ischemia in peripheral artery disease: insights from EUCLID. Circulation 2019; 140: 556–65. - PubMed

