Effects of macrophages in OSCC progression
- PMID: 39877372
- PMCID: PMC11772471
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1517886
Effects of macrophages in OSCC progression
Abstract
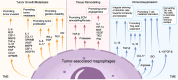
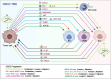
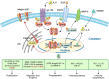
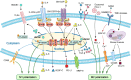
Macrophages are crucial immune cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME), involved in regulating tumor proliferation, invasion, metastasis, ECM remodeling, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression. Although more and more experimental evidence and clinical data indicate that macrophages are involved in the onset and progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), the exact pathogenesis of OSCC associated with macrophages has not been fully elucidated. Enhanced knowledge of the molecular mechanisms involving macrophages in OSCC will aid in the creation of treatments targeted specifically at macrophages. This review outlines the pro-tumoral and anti-tumoral effects of macrophages in OSCC, emphasizing the interaction between OSCC cells and macrophages. It can provide theoretical basis for the establishment of complex regulatory network centered on macrophages and explore novel therapeutic strategies for OSCC.
Keywords: interaction; loop; macrophages; oral squamous cell carcinoma; polarization.
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Dong and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor microenvironment in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1485174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485174. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39744628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA DCST1-AS1 Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization through Activating NF-κB Signaling.J Immunol Res. 2021 Aug 8;2021:5524231. doi: 10.1155/2021/5524231. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34414241 Free PMC article.
-
Deliberation concerning the role of M1-type macrophage subset in oral carcinogenesis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 8;43(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03128-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39113068 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tumour-associated macrophages in oral squamous cells carcinoma progression: an update on current knowledge.Diagn Pathol. 2017 Apr 5;12(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13000-017-0623-6. Diagn Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28381274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote an immunosuppressive microenvironment through the induction and accumulation of protumoral macrophages.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8633-8647. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14374. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28052009 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Polarization, Immunoregulation, and Immunotherapy.Cells. 2025 May 19;14(10):741. doi: 10.3390/cells14100741. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Microbial Dysbiosis Driven by Periodontitis Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;17(13):2181. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132181. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

