Plasmonic Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy: Benchmarking of Photothermal Properties and Modeling of Heating at Depth in Human Tissues
- PMID: 39877425
- PMCID: PMC11770747
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c06381
Plasmonic Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy: Benchmarking of Photothermal Properties and Modeling of Heating at Depth in Human Tissues
Abstract
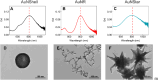
Many different types of nanoparticles have been developed for photothermal therapy (PTT), but directly comparing their efficacy as heaters and determining how they will perform when localized at depth in tissue remains complex. To choose the optimal nanoparticle for a desired hyperthermic therapy, it is vital to understand how efficiently different nanoparticles extinguish laser light and convert that energy to heat. In this paper, we apply photothermal mass conversion efficiency (η m ) as a metric to compare nanoparticles of different shapes, sizes, and conversion efficiencies. We selected silica-gold nanoshells (AuNShells), gold nanorods (AuNRs), and gold nanostars (AuNStars) as three archetypal nanoparticles for PTT and measured the η m of each to demonstrate the importance of considering both photothermal efficiency and extinction cross section when comparing nanoparticles. By utilizing a Monte Carlo model, we further applied η m to model how AuNRs performed when located at tissue depths of 0-30 mm by simulating the depth penetration of near-infrared (NIR) laser light. These results show how nanoparticle concentration, laser power, and tissue depth influence the ramp time to a hyperthermic temperature of 43 °C. The methodology outlined in this paper creates a framework to benchmark the heating efficacy of different nanoparticle types and a means of estimating the feasibility of nanoparticle-mediated PTT at depth in the NIR window. These are key considerations when predicting the potential clinical impact in the early stages of nanoparticle design.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy: a comparative study of heating for different particle types.Lasers Surg Med. 2012 Oct;44(8):675-84. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22072. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Lasers Surg Med. 2012. PMID: 22933382 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing fluorescence detection and effective photothermal therapy of near-infrared polymer nanoparticles using alginate tissue phantoms.Lasers Surg Med. 2018 Dec;50(10):1040-1049. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22955. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Lasers Surg Med. 2018. PMID: 29953621 Free PMC article.
-
Multiphysics Modeling of Plasmonic Photothermal Heating Effects in Gold Nanoparticles and Nanoparticle Arrays.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2020 Aug 6;124(31):17172-17182. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c02443. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 34367407 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing gold nanoparticles in plasmonic photothermal therapy for cancer treatment.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 15;11(4):e42738. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42738. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40084020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy of Tumors with Plasmonic Nanoparticles: Challenges and Prospects.Materials (Basel). 2022 Feb 21;15(4):1606. doi: 10.3390/ma15041606. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35208145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering plasmonic Au nanostars: Enhanced plasmonic properties, preparation and biomedical application.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jun 24;33:102022. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102022. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40677398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials targeting cancer stem cells to overcome drug resistance and tumor recurrence.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 6;15:1499283. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1499283. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40548119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An All-in-One Nanoheater and Optical Thermometer Fabricated from Fractal Nanoparticle Assemblies.ACS Nano. 2025 Apr 15;19(14):13779-13789. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c16452. Epub 2025 Apr 4. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40184431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rastinehad A. R.; Anastos H.; Wajswol E.; Winoker J. S.; Sfakianos J. P.; Doppalapudi S. K.; Carrick M. R.; Knauer C. J.; Taouli B.; Lewis S. C.; Tewari A. K.; Schwartz J. A.; Canfield S. E.; George A. K.; West J. L.; Halas N. J. Gold Nanoshell-Localized Photothermal Ablation of Prostate Tumors in a Clinical Pilot Device Study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2019, 116 (37), 18590–18596. 10.1073/pnas.1906929116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
