Post-operative incidence of lymphedema after RARP with or without extended pelvic lymph node dissection in a cohort study
- PMID: 39877579
- PMCID: PMC11771481
- DOI: 10.1002/bco2.466
Post-operative incidence of lymphedema after RARP with or without extended pelvic lymph node dissection in a cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: Lymphedema of the lower limbs and pubic area is a potential complication following extended pelvic lymph node dissection (ePLND) during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP). The incidence of lymphedema after ePLND has not been systematically reported in the literature. This study aimed to determine the incidence of lymphedema, describe its clinical characteristics and identify specific risk factors in patients undergoing RARP with or without ePLND.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted at a tertiary referral centre between April 2016 and July 2020. Structured electronic case report forms (eCRFs) integrated into the electronic health record system were used to document intraoperative, perioperative and postoperative data. The primary endpoint was the incidence of lymphedema. Secondary endpoints included risk factors for and localization of the postoperative lymphedema.
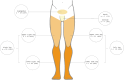
Results: A total of 500 patients who underwent RARP were included, with 301 patients undergoing ePLND and 199 patients without any form of PLND. Median follow-up period was 18 (range 3-49) months. Seventy-eight out of 301 (26%) of patients who underwent ePLND developed lymphedema, compared to only 2 out of 199 (1%) patients without ePLND. In most patients (49/301, 16%), lymphedema was mild (grade 1), whereas 29 patients (10%) developed grade 2 lymphedema. Twenty-six patients (9%) received decongestive lymphatic therapy. The most frequent site of lymphedema occurrence were the lower (54%) and the upper legs (40%). The number of nodes removed during RARP was identified as a risk factor for post-operative lymphedema (OR 1.04; p < 0.05).
Conclusions: In this cohort study, approximately one in four patients undergoing RARP with ePLND developed lower limb and/or midline oedema, whereas one in ten patients started decongestive lymphatic therapy for symptomatic lymphedema. These findings provide valuable information for patient counselling about the potential benefits and risks of ePLND.
Keywords: extended pelvic lymph node dissection; lymphedema; robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy.
© 2024 The Author(s). BJUI Compass published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International Company.
Conflict of interest statement
In accordance with the standards for transparent disclosure, the following conflicts of interest are declared: Steven Joniau and Wouter Everaerts hold the position of Senior Clinical Researcher at the Research Foundation – Flanders (FWO); Luc Bijnens holds stocks in various pharmaceutical companies not leading to a financial interest related to the subject matter of this research. All authors affirm their commitment to upholding objectivity and integrity in the research process, ensuring that these potential conflicts do not compromise the quality or impartiality of the findings presented.
References
-
- Hermsen R, Wedick EBC, Vinken MJM, van Kalmthout LWM, Küsters‐Vandevelde HVN, Wijers CHW, et al. Lymph node staging with fluorine‐18 prostate specific membrane antigen 1007‐positron emission tomography/computed tomography in newly diagnosed intermediate‐ to high‐risk prostate cancer using histopathological evaluation of extended pelvic node dissection as reference. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49(11):3929–3937. 10.1007/s00259-022-05827-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous