Functionally active modulators targeting the LRRK2 WD40 repeat domain identified by FRASE-bot in CACHE Challenge #1
- PMID: 39877816
- PMCID: PMC11770807
- DOI: 10.1039/d4sc07532c
Functionally active modulators targeting the LRRK2 WD40 repeat domain identified by FRASE-bot in CACHE Challenge #1
Abstract
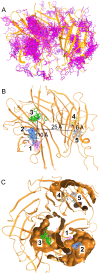
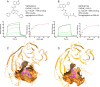
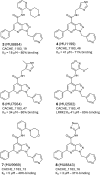
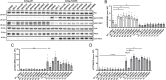
Critical Assessment of Computational Hit-Finding Experiments (CACHE) Challenges emerged as real-life stress tests for computational hit-finding strategies. In CACHE Challenge #1, 23 participants contributed their original workflows to identify small-molecule ligands for the WD40 repeat (WDR) of LRRK2, a promising Parkinson's target. We applied the FRASE-based hit-finding robot (FRASE-bot), a platform for interaction-based screening allowing a drastic reduction of the explorable chemical space and a concurrent detection of putative ligand-binding sites. In two screening rounds, 84 compounds were procured for experimental testing and 8 were confirmed to bind LRRK2-WDR with dissociation constants (K d) ranging from 3 to 41 μM. To investigate the functional effect of WDR ligands, they were tested for their ability to modify the LRRK2 activity markers in HEK293T cells. Two compounds showed statistically significant increases in the kinase activity of WT LRRK2, and two compounds affected the conformation and kinase activity of major LRRK2 mutants.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In silico screening of LRRK2 WDR domain inhibitors using deep docking and free energy simulations.Chem Sci. 2024 Apr 11;15(23):8800-8812. doi: 10.1039/d3sc06880c. eCollection 2024 Jun 12. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38873063 Free PMC article.
-
CACHE Challenge #1: Targeting the WDR Domain of LRRK2, A Parkinson's Disease Associated Protein.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Nov 25;64(22):8521-8536. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01267. Epub 2024 Nov 5. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39499532
-
Active Learning-Guided Hit Optimization for the Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 WDR Domain Based on In Silico Ligand-Binding Affinities.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5706-5717. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00588. Epub 2025 May 25. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40415386 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) inhibitors for Parkinson's disease: a patent review of the literature to date.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024 Sep;34(9):773-788. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2024.2378076. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024. PMID: 39023243 Review.
-
Targeting leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Future Med Chem. 2019 Aug;11(15):1953-1977. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0484. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31517532 Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-causing mutations in the G protein β5 β-propeller disrupt its chaperonin-mediated folding trajectory.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 30:2025.05.28.656654. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656654. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501749 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Deniston C. K. Salogiannis J. Mathea S. Snead D. M. Lahiri I. Matyszewski M. Donosa O. Watanabe R. Böhning J. Shiau A. K. Knapp S. Villa E. Reck-Peterson S. L. Leschziner A. E. Structure of LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease and model for microtubule interaction. Nature. 2020;588:344–349. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2673-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

