Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling by palmitoylation
- PMID: 39877903
- PMCID: PMC11772949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111667
Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling by palmitoylation
Abstract
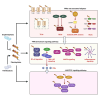
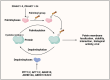
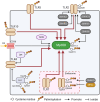
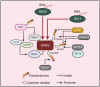
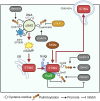
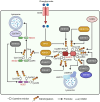
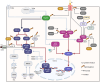
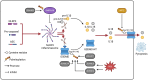
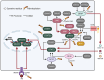
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), consisting of Toll-like receptors, RIG-I-like receptors, cytosolic DNA sensors, and NOD-like receptors, sense exogenous pathogenic molecules and endogenous damage signals to maintain physiological homeostasis. Upon activation, PRRs stimulate the sensitization of nuclear factor κB, mitogen-activated protein kinase, TANK-binding kinase 1-interferon (IFN) regulatory factor, and inflammasome signaling pathways to produce inflammatory factors and IFNs to activate Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathways, resulting in anti-infection, antitumor, and other specific immune responses. Palmitoylation is a crucial type of post-translational modification that reversibly alters the localization, stability, and biological activity of target molecules. Here, we discuss the available knowledge on the biological roles and underlying mechanisms linked to protein palmitoylation in modulating PRRs and their downstream signaling pathways under physiological and pathological conditions. Moreover, recent advances in the use of palmitoylation as an attractive therapeutic target for disorders caused by the dysregulation of PRRs were summarized.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Immune response; Molecular biology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crosstalk between pattern-recognition receptor signaling and calcium signaling.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:745-756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34634335 Review.
-
Combined CpG and poly I:C stimulation of monocytes results in unique signaling activation not observed with the individual ligands.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23876795
-
Pattern-recognition receptors in endometriosis: A narrative review.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1161606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161606. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction: The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 5;18:8875-8897. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S521655. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40635763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated insights into the molecular networks for NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Cell Mol Immunol. 2025 Jun;22(6):563-596. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01284-9. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Cell Mol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40307577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-acylation in apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death: a central regulator of membrane dynamics and protein function.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Apr 29;53(2):487-96. doi: 10.1042/BST20253012. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40304073 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

