Multi-omics analysis reveals distinct gene regulatory mechanisms between primary and organoid-derived human hepatocytes
- PMID: 39878507
- PMCID: PMC11810045
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050883
Multi-omics analysis reveals distinct gene regulatory mechanisms between primary and organoid-derived human hepatocytes
Abstract
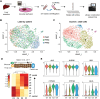
Hepatic organoid cultures are a powerful model to study liver development and diseases in vitro. However, hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from these organoids remain immature compared to primary human hepatocytes (PHHs), which are the benchmark in the field. Here, we applied integrative single-cell transcriptome and chromatin accessibility analysis to reveal gene regulatory mechanisms underlying these differences. We found that, in mature human hepatocytes, activator protein 1 (AP-1) factors co-occupy regulatory regions with hepatocyte-specific transcription factors, including HNF4A, suggesting their potential cooperation in governing hepatic gene expression. Comparative analysis identified distinct transcription factor sets that are specifically active in either PHHs or intrahepatic cholangiocyte organoid (ICO)-derived human hepatocytes. ELF3 was one of the factors uniquely expressed in ICO-derived hepatocytes, and its expression negatively correlated with hepatic marker gene expression. Functional analysis further revealed that ELF3 depletion increased the expression of key hepatic markers in ICO-derived hepatocytes. Our integrative analysis provides insights into the transcriptional regulatory networks of PHHs and hepatic organoids, thereby informing future strategies for developing improved hepatic models.
Keywords: ELF3; Gene regulatory network; Intrahepatic cholangiocyte organoids; Primary human hepatocytes; scRNA-seq.
© 2025. Published by The Company of Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Andreoli, J. M., Jang, S.-I., Chung, E., Coticchia, C. M., Steinert, P. M. and Markova, N. G. (1997). The expression of a novel, epithelium-specific ets transcription factor is restricted to the most differentiated layers in the epidermis. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4287-4295. 10.1093/nar/25.21.4287 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews, T. S., Atif, J., Liu, J. C., Perciani, C. T., Ma, X.-Z., Thoeni, C., Slyper, M., Eraslan, G., Segerstolpe, A., Manuel, J.et al. (2022). Single-cell, single-nucleus, and spatial RNA sequencing of the human liver identifies cholangiocyte and mesenchymal heterogeneity. Hepatol. Commun. 6, 821-840. 10.1002/hep4.1854 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

