A systematic review on the influence of coagulopathy and immune activation on New Onset Atrial Fibrillation in patients with sepsis
- PMID: 39879166
- PMCID: PMC11778662
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318365
A systematic review on the influence of coagulopathy and immune activation on New Onset Atrial Fibrillation in patients with sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: New Onset Atrial Fibrillation (NOAF) is the most common arrhythmia in intensive care. Complications of NOAF include thromboembolic events such as myocardial infarction and stroke, which contribute to a greater risk of mortality. Inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers in sepsis are thought to be associated with NOAF development. The aim of this systematic review and narrative synthesis is to identify inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers as predisposing risk factors for NOAF in sepsis.
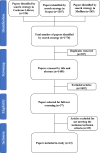
Methods: Three databases (Medline, Cochrane Library, and Scopus) were searched using a predefined search strategy. Inclusion / exclusion criteria were applied, and quality assessments were performed using the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS).
Results: We identified 1776 articles; and 12 articles were included in this review. 8 articles were retrospective observational studies and 4 were prospective observational studies. There was considerable heterogeneity between studies regarding outcomes, methodological design, quality, definitions and reported biomarkers of interest. There is evidence that C-reactive protein (CRP) is associated with NOAF, with hazard ratios 3.33 (3.32-3.35) p = 0.001 and odds ratios of 1.011 (1.008-1.014) p<0.001. International Normalised Ratio (INR) and fibrinogen may be associated with NOAF with odds ratios reported as 1.837 (1.270-2.656) p = 0.001 and 1.535(1.232-1.914) p<0.001 respectively.
Conclusion: Further research is required to confirm the association between inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers and the development of NOAF in sepsis. A broader evidence base will guide treatment strategies, improving the standard of care for patients who develop NOAF in sepsis. Furthermore, given the heterogeneity between studies consideration should be given to inclusion of immune biomarkers in future core outcome sets for trials investigating NOAF.
Copyright: © 2025 Johnston et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Update of
-
Study protocol: A systematic review and meta-analysis regarding the influence of coagulopathy and immune activation on new onset atrial fibrillation in patients with sepsis.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 8;18(9):e0290963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290963. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 Jan 29;20(1):e0318365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318365. PMID: 37683020 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous