Mitochondrial dysfunction-driven AMPK-p53 axis activation underpins the anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effects of sulfane sulfur
- PMID: 39880887
- PMCID: PMC11779946
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83530-0
Mitochondrial dysfunction-driven AMPK-p53 axis activation underpins the anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effects of sulfane sulfur
Abstract
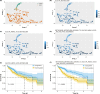
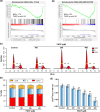
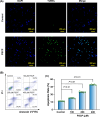
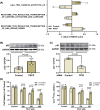
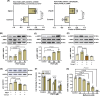
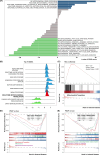
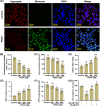
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent form of primary liver cancer, notoriously refractory to conventional chemotherapy. Historically, sulfane sulfur-based compounds have been explored for the treatment of HCC, but their efficacy has been underwhelming. We recently reported a novel sulfane sulfur donor, PSCP, which exhibited improved chemical stability and structural malleability. This study aimed to investigate the effects of PSCP on HCC and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. We utilized bioinformatics algorithms for clustering, function enrichment, feature screening and survival analysis on proteomic data from the Cancer Proteome Atlas (CPTAC) and transcriptomic data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The impact of PSCP on HCC was assessed in vitro and in vivo, focusing on the expression and activity of p53 and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), as well as mitochondrial function. The molecular target of PSCP was identified using Autodock, and binding interactions were visually analyzed. Sulfur metabolism was found to be reprogrammed in HCC, with downregulation of sulfur-related pathways correlating with poor patient prognosis. PSCP treatment significantly inhibited HCC tumor growth in an allograft model, reduced cell viability and proliferation, and induced apoptosis. PSCP potently increased p53 expression and induced AMPK phosphorylation in SNU398 HCC cells. AMPK suppression diminished PSCP-induced p53 upregulation. PSCP also impaired mitochondrial function by inhibiting mitochondrial respiratory complex I, with Ndus3 likely being the target of PSCP's action. Supplementation with ATP significantly countered PSCP-induced SNU398 cell injury. Our findings suggest that the reprogramming of sulfur-related metabolic pathways is pivotal in HCC. PSCP presents as a promising therapeutic strategy by activating the AMPK-p53 signaling axis.
Keywords: AMPK; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Metabolic reprogramming; Mitochondrial complex; Sulfane sulfur; p53.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Medical University (Approval Number: GY2020-099). Accordance statement: All procedures were strictly adhered to the guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Medical University. ARRIVE statement: All procedures were conducted in full compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures

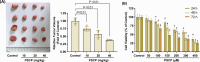
Similar articles
-
Liensinine reshapes the immune microenvironment and enhances immunotherapy by reprogramming metabolism through the AMPK-HIF-1α axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 15;44(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03477-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40665352 Free PMC article.
-
IGF2 Is Up-regulated by Epigenetic Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Is an Actionable Oncogene Product in Experimental Models.Gastroenterology. 2016 Dec;151(6):1192-1205. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27614046
-
Protein phosphatase 2A-B55β mediated mitochondrial p-GPX4 dephosphorylation promoted sorafenib-induced ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating p53 retrograde signaling.Theranostics. 2023 Jul 31;13(12):4288-4302. doi: 10.7150/thno.82132. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37554285 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous ethanol injection or percutaneous acetic acid injection for early hepatocellular carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 26;1(1):CD006745. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006745.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25620061 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Llovet, J. M. et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers7, 6. 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Yang, C. et al. Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.20, 203–222. 10.1038/s41575-022-00704-9 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Weisberger, A. S. & Pensky, J. Tumor-inhibiting effects derived from an active principle of garlic (Allium sativum). Science126, 1112–1114. 10.1126/science.126.3283.1112-a (1957). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

