Signature cytokine-associated transcriptome analysis of effector γδ T cells identifies subset-specific regulators of peripheral activation
- PMID: 39881001
- PMCID: PMC11876068
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-02073-8
Signature cytokine-associated transcriptome analysis of effector γδ T cells identifies subset-specific regulators of peripheral activation
Abstract
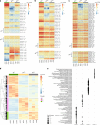
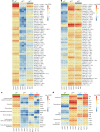
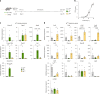
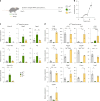
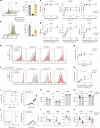
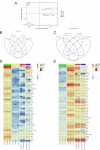
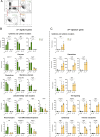
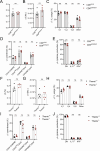
γδ T cells producing either interleukin-17A (γδ17 cells) or interferon-γ (γδIFN cells) are generated in the mouse thymus, but the molecular regulators of their peripheral functions are not fully characterized. Here we established an Il17a-GFP:Ifng-YFP double-reporter mouse strain to analyze at unprecedented depth the transcriptomes of pure γδ17 cell versus γδIFN cell populations from peripheral lymph nodes. Within a very high fraction of differentially expressed genes, we identify a panel of 20 new signature genes in steady-state γδ17 cells versus γδIFN cells, which we further validate in models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and cerebral malaria, respectively. Among the signature genes, we show that the co-receptor CD6 and the signaling protein Themis promote the activation and proliferation of peripheral γδIFN cells in response to T cell antigen receptor stimulation in vitro and to Plasmodium infection in vivo. This resource can help to understand the distinct activities of effector γδ T cell subsets in pathophysiology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Ribot, J. C., Lopes, N. & Silva-Santos, B. γδ T cells in tissue physiology and surveillance. Nat. Rev. Immunol.21, 221–232 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Chora, A. F. et al. Interplay between liver and blood stages of Plasmodium infection dictates malaria severity via γδ T cells and IL-17-promoted stress erythropoiesis. Immunity56, 592–605 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

