Game-thinking; utilizing serious games and gamification in nursing education - a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39881301
- PMCID: PMC11776282
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-06531-7
Game-thinking; utilizing serious games and gamification in nursing education - a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The digital shift in higher education is moving from teacher-focused models to active learning with digital technologies, including the integration of game-based learning strategies. We aim to identify, assess, and summarize the findings of evidence and determine the effectiveness of game-thinking on learning outcomes in nursing education.
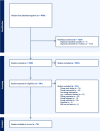
Methods: A comprehensive search for relevant literature was conducted between April and May 2022 Seven databases ERIC, Scopus, ProQuest Education Source, MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, and Embase were utilized to locate original, peer-reviewed papers published in English. The review was conducted and reported in compliance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines.
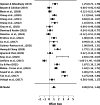
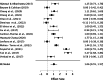
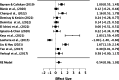
Results: Overall, 3302 studies were initially screened based on their titles and abstract. From this selection 281 studies were then assessed for full-text eligibility. In the end, 70 studies, consisting of 27 Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) and 43 Quasi-experimental studies were included in the review. These studies encompassed data from a total of 8348 participants. The results from the narrative synthesis of the results revealed consistencies across the included studies and their findings. The meta-analysis suggested that game-thinking could be beneficial in nursing education, notably improving students' academic achievement (Pooled ES = 0.99, [95%CI 0.53, 1.44]). The most significant effect of game-thinking on academic achievement was observed in the academic knowledge performance of nursing students (Pooled ES = 1.06, [95%CI 0.55, 1.57]), followed by academic skill performance (Pooled ES = 0.54, [95%CI 0.06, 1.03]).
Conclusions: The systematic review and meta-analysis provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of game-thinking in nursing education. The findings highlight the potential of game-based learning in enhancing nursing education through knowledge acquisition, albeit with a nuanced effect on skill development. As nursing education continues to adapt to the digital era, integration of game-thinking strategies could serve as a valuable method for creating engaging and effective learning experiences for nursing students.
Keywords: Digital media for learning; Game-based learning; Game-thinking; Gamification; Higher education; Nursing; Serious games; Video Games.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: As this review is based only on published studies, ethics approval and consent to participate are not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kapp KM. The gamification of learning and instruction : game-based methods and strategies for training and education. In. San Francisco: Pfeiffer; 2012.
-
- Brooks DC, McCormack M. Driving digital transformation in higher education. EDUCAUSE 2020.
-
- Armstrong M, Landers R, Collmus A. Gamifying recruitment, selection, training, and performance management: game-thinking in human resource management. In., edn.; 2016:140–165.
-
- Landers R. Gamification misunderstood: how badly executed and rhetorical gamification obscures its transformative potential. J Manag Inq. 2019;28:137–40. - DOI
-
- Landers RN. Developing a theory of gamified learning: linking serious games and gamification of learning. Simul Gaming. 2014;45(6):752–68. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous