Innovative antifungal strategies: enhanced biofilm inhibition of Candida albicans by a modified tea tree oil formulation
- PMID: 39881994
- PMCID: PMC11778174
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1518598
Innovative antifungal strategies: enhanced biofilm inhibition of Candida albicans by a modified tea tree oil formulation
Abstract
Introduction: Candida albicans is a significant human pathogen with the ability to form biofilms, a critical factor in its resistance to antifungal treatments. This study aims to evaluate the antifungal activity and biofilm inhibition potential of Tea Tree Oil (TTO) derived from Melaleuca alternifolia cultivated in Vietnam.
Methods: The antifungal activity of TTO was assessed by determining the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC), Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC), Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC), and Minimum Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) using broth dilution methods. The experiments were conducted on C. albicans in both planktonic and biofilm states across concentrations ranging from 0.1 μL/mL to 10 μL/mL.
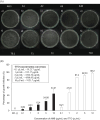
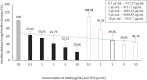
Results: TTO demonstrated significant antifungal efficacy, with a MIC of 0.1 μL/mL (∼91.217 μg/mL) and an MFC of 10 μL/mL (∼9121.7 μg/mL). It effectively inhibited biofilm formation with a recorded MBIC of 2 μL/mL (∼1824.34 μg/mL). However, MBEC values were not determinable as the concentrations tested did not achieve the eradication of more than 50% of mature biofilm within the experimental conditions.
Discussion: These findings highlight TTO as a promising natural antifungal agent with strong biofilm-inhibitory properties. However, its limited efficacy in eradicating mature biofilms underscores the need for further studies, potentially involving higher concentrations or synergistic combinations with conventional antifungal agents.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC); Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC); antifungal; biofilm; biofilm inhibition; modified tea tree oil formulation; tea tree oil.
Copyright © 2025 Tuan, Uyen, Khuon, Binh and Masak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Blanc A. R., Sortino M. A., Butassi E., Svetaz L. A. (2023). Synergistic effects of Thymus vulgaris essential oil in combination with antifungal agents and inhibition of virulence factors of Candida albicans. Phytomed. Plus 3:100481.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

