Multidimensional structural analyses revealed a correlation between thalamic atrophy and white matter degeneration in idiopathic dystonia
- PMID: 39882023
- PMCID: PMC11775609
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf026
Multidimensional structural analyses revealed a correlation between thalamic atrophy and white matter degeneration in idiopathic dystonia
Abstract
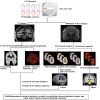
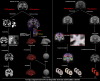
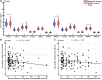
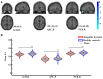
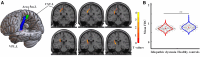
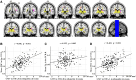
Although aberrant changes in grey and white matter are core features of idiopathic dystonia, few studies have explored the correlation between grey and white matter changes in this disease. This study aimed to investigate the coupling correlation between morphological and microstructural alterations in patients with idiopathic dystonia. Structural T1 imaging and diffusion tensor imaging were performed on a relatively large cohort of patients. Multidimensional structural analyses, including voxel-based analyses, voxel-based morphology, fixel-based analyses and surface-based morphometry, were performed to explore these structural alterations. Probabilistic tractography and correlation analyses were employed to examine these relationships. A total of 147 patients with idiopathic dystonia and 137 healthy controls were recruited in this study. There were no significant differences in the cortical morphometry between patients with idiopathic dystonia and healthy controls using voxel- and surface-based morphometry. However, the grey matter volume of the bilateral thalamus, fractional anisotropy in the right anterior corona radiata, right retrolenticular part of the internal capsule and right posterior corona radiata, and the fibre density and cross-section combined in the fibre tract connecting the left ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus and left area 5 m, were significantly decreased in patients with idiopathic dystonia compared with those in healthy controls. Furthermore, the reduced grey matter volume in the right thalamus not only correlated with the disease duration but also with the reduced fractional anisotropy in the right posterior corona radiata and decreased the fibre density and cross-section combined in the fibre tract connecting the left ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus and the left area 5 m in patients with idiopathic dystonia. These findings suggest that the thalamus is structurally impaired in idiopathic dystonia and that microstructural disruption in thalamocortical projections occurs secondary to thalamic atrophy.
Keywords: fixel-based analyses; idiopathic dystonia; surface-based morphometry; voxel-based analyses; voxel-based morphology.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diffusion kurtosis imaging of brain white matter alteration in patients with coronary artery disease based on the TBSS method.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Feb 15;16:1301826. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1301826. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38425783 Free PMC article.
-
Grey and white matter microstructure changes in epilepsy patients with vagus nerve stimulators.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Oct;209:106918. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106918. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34500340
-
Microstructural white matter abnormalities in patients with COL6A3 mutations (DYT27 dystonia).Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018 Jan;46:74-78. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018. PMID: 29066004
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
-
Subcortical Alterations in Newly Diagnosed Epilepsy and Associated Changes in Brain Connectivity and Cognition.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Nov;45(16):e70069. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70069. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39508641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marsden CD. The problem of adult-onset idiopathic torsion dystonia and other isolated dyskinesias in adult life (including blepharospasm, oromandibular dystonia, dystonic writer's cramp, and torticollis, or axial dystonia). Adv Neurol. 1976;14:259–276. - PubMed
-
- Lehéricy S, Tijssen MA, Vidailhet M, Kaji R, Meunier S. The anatomical basis of dystonia: Current view using neuroimaging. Mov Disord. 2013;28:944–957. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
