How exercise frequency affects BMI: a nationwide cross-sectional study exploring key influencing factors, including dietary behavior
- PMID: 39882129
- PMCID: PMC11774693
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1514805
How exercise frequency affects BMI: a nationwide cross-sectional study exploring key influencing factors, including dietary behavior
Abstract
Purpose: Body Mass Index (BMI) is an important indicator for assessing obesity and related health risks. With the rapid socio-economic development and changes in lifestyle, abnormal BMI (such as underweight, overweight, and obesity) has become an increasingly serious public health issue. This study aims to explore the impact of exercise frequency on BMI among Chinese adults aged 19 to 59, and to analyze the role of dietary behaviors in regulating BMI, providing a basis for BMI intervention strategies.
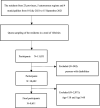
Method: The study employs a multi-stage sampling method across 23 provinces, provincial capitals, and four municipalities in China, randomly selecting 120 cities from each region. Online surveys were conducted using Wenjuanxing by trained surveyors.
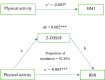
Result: A total of 8,611 individuals participated in the survey. Among them, 1,066 (12.38%) had a BMI < 18.5, 5,354 (62.18%) had a BMI between 18.5 and 23.9, and 2,191 (25.44%) had a BMI ≥ 24. Factors such as gender, age, marital status, monthly household income, smoking, and alcohol consumption significantly affected BMI (p < 0.05). The overall impact of exercise on abnormal BMI was -0.003, with a direct effect of -0.005. The mediating effect of dietary behaviors between exercise and abnormal BMI was 0.002, accounting for 92.48% of the total effect.
Conclusion: This study highlights the widespread prevalence of abnormal BMI among individuals aged 19 to 59 in China. A single exercise intervention may be insufficient to effectively improve abnormal BMI; thus, it should be combined with strategies aimed at enhancing dietary behaviors.
Keywords: body mass index; dietary behavior; exercise; influencing factor; mediation effect.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Guan, Mai, Li, Liu, Zhou, Lin and Teng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . (2024). Obesity and overweight. Available at: (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight)
-
- Zhou BF. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults-study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci. (2002) 15:83–96. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12046553/ PMID: - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

