Multiomics Analysis of Exportin Family Reveals XPO1 as a Novel Target for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 39882192
- PMCID: PMC11774578
- DOI: 10.1155/ijog/3645641
Multiomics Analysis of Exportin Family Reveals XPO1 as a Novel Target for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
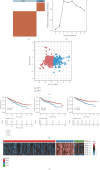
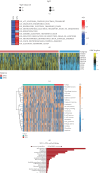
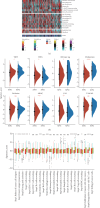
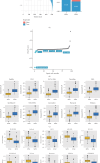
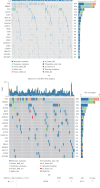
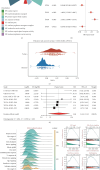
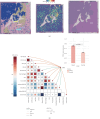
Background: Recently, exportin gene family members have been demonstrated to play essential roles in tumor progression. However, research on the clinical significance of exportin gene family members is limited in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Methods: Pan-cancer data, ccRCC multiomics data, and single-cell sequence were included to analyze the differences in DNA methylation modification, single nucleotide variations (SNVs), copy number variations (CNVs), and expression levels of exportin gene family members. Non-negative matrix factorization was used to identify molecular subtypes based on exportin gene family members, and the prognostic and biological differences of different molecular subtypes were compared across multiple dimensions. Results: Exportin gene family members were upregulated in pan-cancer expression, and their aberrant expression was significantly influenced by DNA methylation, SNV, and CNV, particularly in ccRCC. Based on the expression matrix of exportin gene family members, two molecular subtypes, exportin famliy genes (XPO)-based subtype 1 (XPS1) and exportin famliy genes (XPO)-based subtype 2 (XPS2), were identified. The expression levels of exportin gene family members in the XPS2 subtype were significantly higher than those in XPS1, and the prognosis was poorer. The XPS2 subtype had lower immune component abundance and higher immune exhaustion scores. Its response rate to immunotherapy was significantly lower than that of the XPS1 subtype, but it was more sensitive to small molecules, including mercaptopurine and nutlin. Among them, exportin-1 (XPO1) is a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for ccRCC, which can promote renal cancer progression by activating the PI3K-AKT-mTOR (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT serine/threonine kinase (AKT)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR)) and interferon alpha pathways. Conclusion: This study analyzed the variations of exportin gene family members at the pan-cancer level and identified two distinct ccRCC subtypes, which can guide personalized management of patients.
Keywords: XPO1; clear cell renal cell carcinoma; exportin; pan-cancer; single-cell sequence.
Copyright © 2025 Yanhong Hao et al. International Journal of Genomics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

