Nanoporous Graphene Integrated onto Bimodal Waveguide Biosensors for Detection of C-Reactive Protein
- PMID: 39882250
- PMCID: PMC11773638
- DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.4c06716
Nanoporous Graphene Integrated onto Bimodal Waveguide Biosensors for Detection of C-Reactive Protein
Abstract
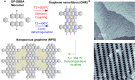
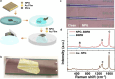
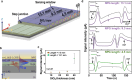
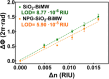
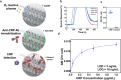
Despite the outstanding progress in photonic sensor devices, a major limitation for its application as label-free biosensors for biomedical analysis lies in the surface biofunctionalization step, that is, the reliable immobilization of the biorecognition element onto the sensor surface. Here, we report the integration of bottom-up synthesized nanoporous graphene onto bimodal waveguide interferometric biosensors as an atomically precise biofunctionalization scaffold. This combination leverages the high sensitivity of bimodal waveguide interferometers and the large functional surface area of nanoporous graphene to create highly sensitive, selective, and robust biosensors for the direct immunoassay detection of C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory biomarker widely used in the clinical diagnosis of infections and sepsis. The limit of detection was determined at 3 ng/mL, which is well below the clinical cutoff levels required for the diagnostic detection of CRP in patient samples. This innovative approach holds promise for transforming diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and various fields requiring precise biomolecular detection.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moreno C.; de Cerio X. D.; Vilas-Varela M.; Tenorio M.; Sarasola A.; Brandbyge M.; Peña D.; Garcia-Lekue A.; Mugarza A. Molecular Bridge Engineering for Tuning Quantum Electronic Transport and Anisotropy in Nanoporous Graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145 (16), 8988–8995. 10.1021/jacs.3c00173. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
