Litter quality modulates changes in bacterial and fungal communities during the gut transit of earthworm species of different ecological groups
- PMID: 39882509
- PMCID: PMC11778916
- DOI: 10.1093/ismeco/ycae171
Litter quality modulates changes in bacterial and fungal communities during the gut transit of earthworm species of different ecological groups
Abstract
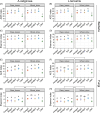
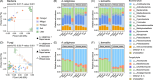
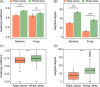
Earthworms are keystone animals stimulating litter decomposition and nutrient cycling. However, earthworms comprise diverse species which live in different soil layers and consume different types of food. Microorganisms in the gut of earthworms are likely to contribute significantly to their ability to digest organic matter, but this may vary among earthworm species. Here, we analyse the effect of food (litter) quality on gut microbiota and their changes during the gut passage (from foregut to hindgut) of earthworms of different ecological groups. The endogeic (soil living) species Aporrectodea caliginosa and the anecic (litter feeding) species Lumbricus terrestris were fed with high- (rape leaves) and low-quality litter (wheat straw) in a microcosm experiment for 18 weeks. Irrespective of earthworm species, alpha diversity of bacterial and fungal communities changed little during the gut passage, with the composition and diversity of microbial communities in the gut generally resembling those in soil more than in litter. In addition, the low-quality litter supported higher alpha diversity and more complex communities than high-quality litter. Further, gut microbial communities of the anecic L. terrestris changed less during gut passage than those of the endogeic A. caliginosa, especially when fed low-quality litter. Our findings indicate that earthworm gut microbial communities are predominantly shaped by the soil they ingest, but are modulated by the quality of litter they feed on and earthworm ecological group. Overall, the results suggest that earthworms primarily influence soil microbiota by mixing and spreading microorganisms from different microhabitats through bioturbation rather than by digesting microorganisms.
Keywords: NGS sequencing; earthworm ecological groups; gut passage; intestinal microbes; microbial diversity; resources quality.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Society for Microbial Ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicting interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ecological and evolutionary responses of earthworm holobionts to environmental changes.ISME J. 2025 Jan 2;19(1):wraf044. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wraf044. ISME J. 2025. PMID: 40057975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the earthworm gut multi-kingdom microbial communities.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Jul 20;727:138301. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138301. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32330704
-
Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: a natural selection process.ISME J. 2010 Mar;4(3):357-66. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.124. Epub 2009 Nov 19. ISME J. 2010. PMID: 19924156
-
Patterns of litter disappearance in a northern hardwood forest invaded by exotic earthworms.Ecol Appl. 2006 Feb;16(1):154-65. doi: 10.1890/04-0788. Ecol Appl. 2006. PMID: 16705969
-
Research progress on earthworms and soil health.Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2025 Feb 18;36(2):637-646. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202502.036. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40370181 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Ecological and evolutionary responses of earthworm holobionts to environmental changes.ISME J. 2025 Jan 2;19(1):wraf044. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wraf044. ISME J. 2025. PMID: 40057975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Edwards CA, Arancon NQ. Biology and Ecology of Earthworms. Springer US, New York, NY. 2022. 10.1007/978-0-387-74943-3 - DOI
-
- Kiyasudeen S K, Ibrahim MH, Quaik S et al. Microbial ecology associated with earthworm and its gut, in: Lens P. (ed.), Prospects of Organic Waste Management and the Significance of Earthworms. Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016;pp:123–45. 10.1007/978-3-319-24708-3_6 - DOI
-
- Medina-Sauza RM, Álvarez-Jiménez M, Delhal A et al. Earthworms building up soil microbiota, a review. Front Env Sci 2019;7:7. 10.3389/fenvs.2019.00081 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

