RNA G-quadruplex structure-based PROTACs for targeted DHX36 protein degradation and gene activity modulation in mammalian cells
- PMID: 39883012
- PMCID: PMC11780864
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf039
RNA G-quadruplex structure-based PROTACs for targeted DHX36 protein degradation and gene activity modulation in mammalian cells
Abstract
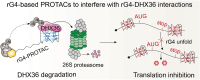
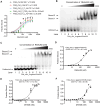
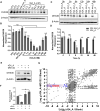
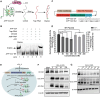
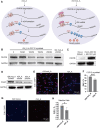
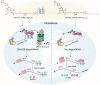
RNA G-quadruplexes (rG4s) are non-canonical secondary nucleic acid structures found in the transcriptome. They play crucial roles in gene regulation by interacting with G4-binding proteins (G4BPs) in cells. rG4-G4BP complexes have been associated with human diseases, making them important targets for drug development. Generating innovative tools to disrupt rG4-G4BP interactions will provide a unique opportunity to explore new biological mechanisms and potentially treat related diseases. Here, we have rationally designed and developed a series of rG4-based proteolytic targeting chimeras (rG4-PROTACs) aimed at degrading G4BPs, such as DHX36, a specific G4BP that regulates gene expression by binding to and unraveling rG4 structures in messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Our comprehensive data and systematic analysis reveals that rG4-PROTACs predominantly and selectively degrade DHX36 through a proteosome-dependent mechanism, which promotes the formation of the rG4 structure in mRNA, leading to the translation inhibition of rG4-containing transcripts. Notably, rG4-PROTACs inhibit rG4-mediated APP protein expression, and impact the proliferative capacity of skeletal muscle stem cells by negatively regulating Gnai2 protein expression. In summary, rG4-PROTACs provide a new avenue to understand rG4-G4BP interactions and the biological implications of dysregulated G4BPs, promoting the development of PROTACs technology based on the non-canonical structure of nucleic acids.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32471343/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- RFS2425-1S02/Research Grants Council (RGC) of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
- 9509003/Croucher Foundation Project
- SCRF/0037/State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution Seed Collaborative Research Fund
- 22377153/Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

