The modification of conventional liposomes for targeted antimicrobial delivery to treat infectious diseases
- PMID: 39883380
- PMCID: PMC11782757
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-024-04170-x
The modification of conventional liposomes for targeted antimicrobial delivery to treat infectious diseases
Abstract
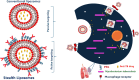
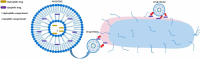
Some of the most crucial turning points in the treatment strategies for some major infectious diseases including AIDS, malaria, and TB, have been reached with the introduction of antimicrobials and vaccines. Drug resistance and poor effectiveness are key limitations that need to be overcome. Conventional liposomes have been explored as a delivery system for infectious diseases bioactives to treat infectious diseases to provide an efficient approach to maximize the therapeutic outcomes, drug stability, targetability, to reduce the side-effects of antimicrobials, and enhance vaccine performance where necessary. However, as the pathological understanding of infectious diseases become more known, the need for more advanced liposomal technologies was born to continue having a profound effect on targeted chemotherapy for infectious diseases. This review therefore provides a concise incursion into the most recent and vogue liposomal formulations used to treat infectious diseases. An appraisal of immunological, stimuli-responsive, biomimetic and functionalized liposomes and other novel modifications to conventional liposomes is assimilated in sync with mutations of resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Antimicrobials; Delivery system; Encapsulation; Infectious diseases; Liposomes; Targeted delivery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- van Seventer JM, Hochberg NS. Principles of infectious diseases: transmission, diagnosis, prevention and control. Int Encycl Public Health. 2017;6(2):22–39. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
