Distinguishing classes of neuroactive drugs based on computational physicochemical properties and experimental phenotypic profiling in planarians
- PMID: 39883642
- PMCID: PMC11781733
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315394
Distinguishing classes of neuroactive drugs based on computational physicochemical properties and experimental phenotypic profiling in planarians
Abstract
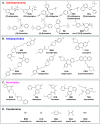
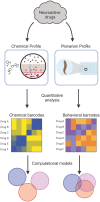
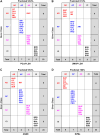
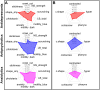
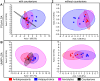
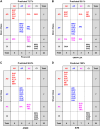
Mental illnesses put a tremendous burden on afflicted individuals and society. Identification of novel drugs to treat such conditions is intrinsically challenging due to the complexity of neuropsychiatric diseases and the need for a systems-level understanding that goes beyond single molecule-target interactions. Thus far, drug discovery approaches focused on target-based in silico or in vitro high-throughput screening (HTS) have had limited success because they cannot capture pathway interactions or predict how a compound will affect the whole organism. Organismal behavioral testing is needed to fill the gap, but mammalian studies are too time-consuming and cost-prohibitive for the early stages of drug discovery. Behavioral medium-throughput screening (MTS) in small organisms promises to address this need and complement in silico and in vitro HTS to improve the discovery of novel neuroactive compounds. Here, we used cheminformatics and MTS in the freshwater planarian Dugesia japonica-an invertebrate system used for neurotoxicant testing-to evaluate the extent to which complementary insight could be gained from the two data streams. In this pilot study, our goal was to classify 19 neuroactive compounds into their functional categories: antipsychotics, anxiolytics, and antidepressants. Drug classification was performed with the same computational methods, using either physicochemical descriptors or planarian behavioral profiling. As it was not obvious a priori which classification method was most suited to this task, we compared the performance of four classification approaches. We used principal coordinate analysis or uniform manifold approximation and projection, each coupled with linear discriminant analysis, and two types of machine learning models-artificial neural net ensembles and support vector machines. Classification based on physicochemical properties had comparable accuracy to classification based on planarian profiling, especially with the machine learning models that all had accuracies of 90-100%. Planarian behavioral MTS correctly identified drugs with multiple therapeutic uses, thus yielding additional information compared to cheminformatics. Given that planarian behavioral MTS is an inexpensive true 3R (refine, reduce, replace) alternative to vertebrate testing and requires zero a priori knowledge about a chemical, it is a promising experimental system to complement in silico cheminformatics to identify new drug candidates.
Copyright: © 2025 Ireland et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: E-MC is the founder of Inveritek, LLC, which offers planarian HTS commercially. RJR currently serves as a member of the advisory board of NeuroX1, a startup biotechnology company that is developing a software platform for the discovery and development of drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization. Mental disorders [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2024 Apr 17]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders.
-
- Council of Economic Advisers. Reducing the Economic Burden of Unmet Mental Health Needs. 2022 May.
-
- World Health Organization. Mental Health and COVID-19: Early evidence of the pandemic ‘ s impact. Sci Br. 2022;2(March):1–11.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

