Identification of Intracranial Germ Cell Tumors Based on Facial Photos: Exploratory Study on the Use of Deep Learning for Software Development
- PMID: 39883924
- PMCID: PMC11826948
- DOI: 10.2196/58760
Identification of Intracranial Germ Cell Tumors Based on Facial Photos: Exploratory Study on the Use of Deep Learning for Software Development
Abstract
Background: Primary intracranial germ cell tumors (iGCTs) are highly malignant brain tumors that predominantly occur in children and adolescents, with an incidence rate ranking third among primary brain tumors in East Asia (8%-15%). Due to their insidious onset and impact on critical functional areas of the brain, these tumors often result in irreversible abnormalities in growth and development, as well as cognitive and motor impairments in affected children. Therefore, early diagnosis through advanced screening techniques is vital for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the application of facial recognition technology in the early detection of iGCTs in children and adolescents. Early diagnosis through advanced screening techniques is vital for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
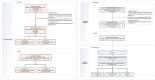
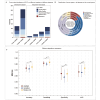
Methods: A multicenter, phased approach was adopted for the development and validation of a deep learning model, GVisageNet, dedicated to the screening of midline brain tumors from normal controls (NCs) and iGCTs from other midline brain tumors. The study comprised the collection and division of datasets into training (n=847, iGCTs=358, NCs=300, other midline brain tumors=189) and testing (n=212, iGCTs=79, NCs=70, other midline brain tumors=63), with an additional independent validation dataset (n=336, iGCTs=130, NCs=100, other midline brain tumors=106) sourced from 4 medical institutions. A regression model using clinically relevant, statistically significant data was developed and combined with GVisageNet outputs to create a hybrid model. This integration sought to assess the incremental value of clinical data. The model's predictive mechanisms were explored through correlation analyses with endocrine indicators and stratified evaluations based on the degree of hypothalamic-pituitary-target axis damage. Performance metrics included area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
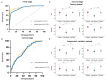
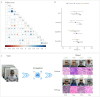
Results: On the independent validation dataset, GVisageNet achieved an AUC of 0.938 (P<.01) in distinguishing midline brain tumors from NCs. Further, GVisageNet demonstrated significant diagnostic capability in distinguishing iGCTs from the other midline brain tumors, achieving an AUC of 0.739, which is superior to the regression model alone (AUC=0.632, P<.001) but less than the hybrid model (AUC=0.789, P=.04). Significant correlations were found between the GVisageNet's outputs and 7 endocrine indicators. Performance varied with hypothalamic-pituitary-target axis damage, indicating a further understanding of the working mechanism of GVisageNet.
Conclusions: GVisageNet, capable of high accuracy both independently and with clinical data, shows substantial potential for early iGCTs detection, highlighting the importance of combining deep learning with clinical insights for personalized health care.
Keywords: algorithms; artificial intelligence; cohort studies; deep learning; endocrine indicators; facial recognition; intracranial germ cell tumors; machine learning models; neural networks; software development; software engineering.
©Yanong Li, Yixuan He, Yawei Liu, Bingchen Wang, Bo Li, Xiaoguang Qiu. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 30.01.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Technological aids for the rehabilitation of memory and executive functioning in children and adolescents with acquired brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 1;7(7):CD011020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27364851 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Packer RJ, Cohen BH, Cooney K. Intracranial germ cell tumors. Oncologist. 2000;5(4):312–320. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pu... - PubMed
-
- Takami H, Fukuoka K, Fukushima S, Nakamura T, Mukasa A, Saito N, Yanagisawa T, Nakamura H, Sugiyama K, Kanamori M, Tominaga T, Maehara T, Nakada M, Kanemura Y, Asai A, Takeshima H, Hirose Y, Iuchi T, Nagane M, Yoshimoto K, Matsumura A, Kurozumi K, Nakase H, Sakai K, Tokuyama T, Shibui S, Nakazato Y, Narita Y, Nishikawa R, Matsutani M, Ichimura K. Integrated clinical, histopathological, and molecular data analysis of 190 central nervous system germ cell tumors from the iGCT Consortium. Neuro Oncol. 2019;21(12):1565–1577. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz139. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31420671 5550931 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjornsson J, Scheithauer BW, Okazaki H, Leech RW. Intracranial germ cell tumors: pathobiological and immunohistochemical aspects of 70 cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985;44(1):32–46. - PubMed
-
- Frappaz D, Dhall G, Murray MJ, Goldman S, Faure Conter C, Allen J, Kortmann RD, Haas-Kogen D, Morana G, Finlay J, Nicholson JC, Bartels U, Souweidane M, Schönberger S, Vasiljevic A, Robertson P, Albanese A, Alapetite C, Czech T, Lau CC, Wen P, Schiff D, Shaw D, Calaminus G, Bouffet E. EANO, SNO and Euracan consensus review on the current management and future development of intracranial germ cell tumors in adolescents and young adults. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(4):516–527. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab252. http://hdl.handle.net/2318/1852058 6415260 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

