Interferon-γ Signaling in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Affects Epithelial Barrier Function and Programmed Cell Death
- PMID: 39884574
- PMCID: PMC11964763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101466
Interferon-γ Signaling in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Affects Epithelial Barrier Function and Programmed Cell Death
Abstract
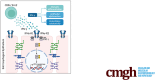
Background & aims: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic esophageal inflammatory disorder characterized by eosinophil-rich mucosal inflammation and tissue remodeling. Prior research has revealed the upregulation of interferon (IFN) response signature genes (ISGs) in biopsy tissue from patients with EoE, but the specific cell types that contribute to this IFN response and the effect of interferons on the esophageal epithelium remain incompletely understood. Here, we use single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to examine the expression of IFN and ISGs during EoE and explore how IFN-α and IFN-γ treatments affect epithelial function.
Methods: Epithelial gene expression from patients with EoE was examined using scRNA-seq and a confirmatory bulk RNA-seq experiment of isolated epithelial cells. The functional impact of IFN-α and IFN-γ on epithelial cells was investigated using organoid models.
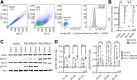
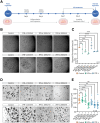
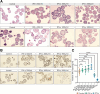
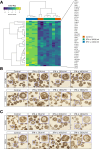
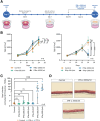
Results: Using scRNA-seq, the highest number of differentially regulated ISGs was found in the epithelial cells of patients with active EoE, and ISGs in transitional epithelial cells correlated significantly with eosinophil counts and endoscopic reference scores. IFN-γ and IFN-α treatments reduced organoid formation rate and size in a dose-dependent manner, with IFN-γ showing a more pronounced impact on measures of epithelial barrier formation and induction of caspase activity. We identify high IFNG expression in a cluster of majority CD8+ T cells with high expression of CD69 and FOS.
Conclusions: These findings reveal that interferon, especially IFN-γ, plays a central role in epithelial cell dysfunction, significantly affecting gene expression, cellular differentiation, and barrier integrity. Clarifying the contribution of varied cytokine signals in EoE may help explain the heterogeneity in patient presentation and therapeutic response.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Barrier Integrity; Eosinophilic Esophagitis; Epithelial Differentiation; Interferon Response.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Update of
-
Interferon-γ signaling in eosinophilic esophagitis has implications for epithelial barrier function and programmed cell death.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 30:2024.01.26.577407. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.26.577407. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;19(5):101466. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101466. PMID: 38352458 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Dellon E.S., Rothenberg M.E., Collins M.H., et al. Dupilumab in adults and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2317–2330. - PubMed
-
- Simon D., Cianferoni A., Spergel J.M., et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by a non-IgE-mediated food hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2016;71:611–620. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

