Effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib versus calcineurin inhibitor in interstitial lung disease secondary to anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis: a multicentre cohort study
- PMID: 39884766
- PMCID: PMC12095906
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01488-2024
Effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib versus calcineurin inhibitor in interstitial lung disease secondary to anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis: a multicentre cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib versus calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) as initial immunosuppressive regimen for anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease (MDA5+DM-ILD).
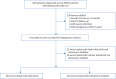
Methods: Adult Chinese patients with newly diagnosed MDA5+DM-ILD (ILD course <3 months) from five tertiary referral centres between April 2014 and January 2023 were included in this retrospective cohort study. The primary effectiveness end-point was lung transplantation-free survival within 1 year. Propensity score-based inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was applied for adjustment in this real-world study.
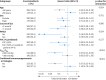
Results: In the eligible cohort, a total of 94 (32.4%) and 105 (46.7%) patients died or underwent lung transplantation within 1 year in the tofacitinib group (n=290) and the CNI group (n=225), respectively. After adjustment by IPTW, patients' lung transplantation-free survival rate within 1 year was significantly higher in the tofacitinib group compared to the CNI group (log-rank p=0.013). Multivariable Cox analysis performed in the IPTW dataset revealed that the hazard ratio of tofacitinib versus CNI for 1-year survival was 0.72 (95% CI 0.56-0.94; p=0.013). The adjusted difference of survival rate was 9.3% (95% CI 2.8-15.8%). Alternative analytic strategies yielded consistent results in sensitivity analyses. Patients aged <60 years, without rapidly progressive ILD, or with baseline arterial oxygen tension/inspiratory oxygen fraction ≥300 mmHg might benefit more from tofacitinib. Opportunistic infection was the major treatment-related serious adverse event, with generally comparable incidence (42.4% versus 45.3%).
Conclusion: In this large multicentre cohort study, tofacitinib showed significantly more benefits for 1-year lung transplantation-free survival than calcineurin inhibitors in MDA5+DM-ILD.
Copyright ©The authors 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tofacitinib in anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease: a new standard of care emerges.Eur Respir J. 2025 May 22;65(5):2500458. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00458-2025. Print 2025 May. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40404197 No abstract available.
-
Survival benefit of tofacitinib in interstitial lung disease associated with anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis: a need for further validation.Eur Respir J. 2025 Jul 14;66(1):2500306. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00306-2025. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40659464 No abstract available.
-
How to treat patients with MDA5-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease? Which immunosuppressive therapy for which patients?Eur Respir J. 2025 Jul 14;66(1):2500446. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00446-2025. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40659468 Free PMC article.
-
Reply: Tofacitinib is a step forward for management of patients with interstitial lung disease associated with anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis.Eur Respir J. 2025 Jul 14;66(1):2500699. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00699-2025. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40659470 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sato S, Hoshino K, Satoh T, et al. RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 2193–2200. doi: 10.1002/art.24621 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsuji H, Nakashima R, Hosono Y, et al. Multicenter prospective study of the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy with high-dose glucocorticoid, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide in interstitial lung diseases accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020; 72: 488–498. doi: 10.1002/art.41105 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
