Computer Simulations of the Temperature Dependence of Enzyme Reactions
- PMID: 39884967
- PMCID: PMC11823412
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.4c01733
Computer Simulations of the Temperature Dependence of Enzyme Reactions
Abstract
In this review we discuss the development of methodology for calculating the temperature dependence and thermodynamic activation parameters for chemical reactions in solution and in enzymes, from computer simulations. We outline how this is done by combining the empirical valence bond method with molecular dynamics free energy simulations. In favorable cases it turns out that such simulations can even capture temperature optima for the catalytic rate. The approach turns out be very useful both for addressing questions regarding the roles of enthalpic and entropic effects in specific enzymes and also for attacking evolutionary problems regarding enzyme adaptation to different temperature regimes. In the latter case, we focus on cold-adaptation of enzymes from psychrophilic species and show how computer simulations have revealed the basic mechanisms behind such adaptation. Understanding these mechanisms also opens up the possibility of designing the temperature dependence, and we highlight a recent example of this.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

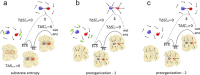
 ) is dominated by reorientation of the substrates,
then the enzyme could pay the penalty already when binding them in
a reactive orientation (
) is dominated by reorientation of the substrates,
then the enzyme could pay the penalty already when binding them in
a reactive orientation ( and
and  ). (b) If
). (b) If  is dominated by reorientation of water
molecules, then the enzyme could bind the substrates in a preorganized
active site that does not need reorientation of the protein dipoles
(
is dominated by reorientation of water
molecules, then the enzyme could bind the substrates in a preorganized
active site that does not need reorientation of the protein dipoles
( ). (c) If the uncatalyzed reaction
has similarly small charge separation in the reactant and transition
states, then the enzyme could yield a favorable activation entropy
by stabilizing a more polar reactant state, causing a relaxation of
the aligned protein dipoles in the transition state (
). (c) If the uncatalyzed reaction
has similarly small charge separation in the reactant and transition
states, then the enzyme could yield a favorable activation entropy
by stabilizing a more polar reactant state, causing a relaxation of
the aligned protein dipoles in the transition state ( ).
).


References
-
- Warshel A.Computer Modeling of Chemical Reactions in Enzymes and Solutions; John Whiley & Sons: New York, 1991.
-
- Bruice T. C.; Lightstone F. C. Ground state and transition state contributions to the rates of intramolecular and enzymatic reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 127–136. 10.1021/ar960131y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
