Biomedical named entity recognition using improved green anaconda-assisted Bi-GRU-based hierarchical ResNet model
- PMID: 39885428
- PMCID: PMC11780922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-024-06008-w
Biomedical named entity recognition using improved green anaconda-assisted Bi-GRU-based hierarchical ResNet model
Abstract
Background: Biomedical text mining is a technique that extracts essential information from scientific articles using named entity recognition (NER). Traditional NER methods rely on dictionaries, rules, or curated corpora, which may not always be accessible. To overcome these challenges, deep learning (DL) methods have emerged. However, DL-based NER methods may need help identifying long-distance relationships within text and require significant annotated datasets.
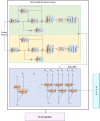
Results: This research has proposed a novel model to address the challenges in natural language processing. The Improved Green anaconda-assisted Bi-GRU based Hierarchical ResNet BNER model (IGa-BiHR BNERM) is the model. IGa-BiHR BNERM model has shown promising results in accurately identifying named entities. The MACCROBAT dataset was obtained from Kaggle and underwent several pre-processing steps such as Stop Word Filtering, WordNet processing, Removal of non-alphanumeric characters, stemming Segmentation, and Tokenization, which is standardized and improves its quality. The pre-processed text was fed into a feature extraction model like the Robustly Optimized BERT -Whole Word Masking model. This model provides word embeddings with semantic information. Then, the BNER process utilized an Improved Green Anaconda-assisted Bi-GRU-based Hierarchical ResNet BNER model (IGa-BiHR BNERM).
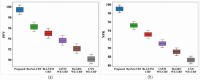
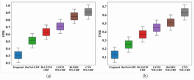
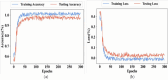
Conclusion: To improve the training phase of the IGa-BiHR BNERM, the Improved Green Anaconda Optimization technique was used to select optimal weight parameter coefficients for training the model parameters. After the model was tested using the MACCROBAT dataset, it outperformed previous models with a tremendous accuracy rate of 99.11%. This model effectively and accurately identifies biomedical names within the text, significantly advancing this field.
Keywords: Bi-GRU; Biomedical name; Hierarchical ResNet; IGAO; ROBERT-WWM; Recognition; Word embedding.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Govindarajan S, et al. (2023) RETRACTED: an optimization based feature extraction and machine learning techniques for named entity identification
-
- Kaswan KS, et al (2021) "AI-based natural language processing for the generation of meaningful information electronic health record (EHR) data." Advanced AI techniques and applications in bioinformatics. CRC Press, 41-86
-
- Wang DQ, et al. Accelerating the integration of ChatGPT and other large-scale AI models into biomedical research and healthcare. MedComm–Future Med. 2023;2(2):43. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

