Protective Effects of SIRT2 Inhibition on Cardiac Fibrosis
- PMID: 39885712
- PMCID: PMC11965944
- DOI: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2025.4770
Protective Effects of SIRT2 Inhibition on Cardiac Fibrosis
Abstract
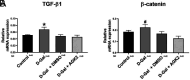
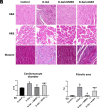
Background: A primary factor in the pathogenesis of aging is oxidative stress, with cardiac inflammation and fibrosis being contributed to by increased oxidative stress as organisms age. Oxidative stress enhances the cardiac fibrotic signaling pathway, with reactive oxygen species inducing cardiac fibrosis through increased expression of the profibrotic factor transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1). Furthermore, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is implicated in interstitial fibrosis, which is associated with TGF-β. Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) is expressed in heart tissue, with protective effects in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. We aimed to investigate the mechanisms of cardiac fibrosis in D-Galactose (D-Gal)-induced accelerated aging, focusing on TGF-β1, β-catenin, and SIRT2.
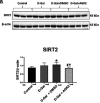
Methods: A total of 30 young male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: control group, D-Gal group, D-Gal + 4% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) group, and D-Gal + the SIRT2 inhibitor (AGK2) group. After 10 weeks, the rats were sacrificed, and their hearts were removed. SIRT2 expression levels were measured by western blot and gene expression levels of TGF-β1 and β-catenin by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) mRNA expression in heart tissue was higher in the D-Gal group compared to all other groups. β-catenin mRNA expression was higher in the D-Gal group than in the D-Gal + AGK2 group. SIRT2 protein expression was higher in the D-Gal + DMSO group compared to the control group. Sirtuin 2 expression was lower in the D-Gal + AGK2 group compared to the D-Gal and D-Gal + DMSO groups.
Conclusion: Sirtuin 2 inhibition attenuates fibrosis, as evidenced by the downregulation of TGF-β1 and β-catenin. Thus, targeting SIRT2 may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for diseases characterized by cardiac fibrosis in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AGK2, a SIRT2 inhibitor, ameliorates D-galactose-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting fibrogenic factors.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Nov;38(11):e70000. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70000. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39400930
-
Inhibition of SIRT2 Alleviates Fibroblast Activation and Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis via MDM2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):451-460. doi: 10.1159/000488613. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29614506
-
[Effects of Luhong Yixin Granules on myocardial fibrosis in heart failure rats based on TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;49(13):3583-3590. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240308.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39041130 Chinese.
-
The involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade in fibrosis progression and its therapeutic targeting by relaxin.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 May;223:116130. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116130. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38490518 Review.
-
Interactions between TGF-β1, canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway and PPAR γ in radiation-induced fibrosis.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 23;8(52):90579-90604. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21234. eCollection 2017 Oct 27. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29163854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sacco RL, Roth GA, Reddy KS, et al. The heart of 25 by 25: achieving the goal of reducing global and regional premature deaths from cardiovascular diseases and stroke: a modeling study from the American Heart Association and World Heart Federation. Circulation. 2016;133(23):e674 e690. (10.1161/CIR.0000000000000395) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

