Under-representation of older Indian persons with cancer in clinical trials
- PMID: 39886158
- PMCID: PMC11347695
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjonc-2024-000445
Under-representation of older Indian persons with cancer in clinical trials
Abstract
Objective: Older patients with cancer have traditionally been under-represented in global clinical trials. There are no data from India regarding this issue.
Methods and analysis: This was a retrospective analysis done at our institute on interventional studies conducted between 2003 and 2023 in adult patients with malignancies. We excluded studies done exclusively in the paediatric population and observational studies.
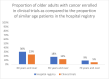
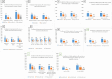
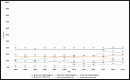
Results: We included 21 894 patients enrolled in 150 interventional trials from the departments of surgical, medical, and radiation oncology, anaesthesia, and clinical pharmacology; 110 (73.3%) were investigator initiated. There were 38 trials (25.3%) in breast cancer (6141 patients, 28%), and 33 (22%) in head and neck cancer (6975 patients, 31.9%). Studies were predominantly phase III (97 trials (64.7%)). Multicentric studies comprised approximately one-third (48, 32%). The median age of enrolled patients was 51 years (IQR 43-59). There were 5132 (23.4%) participants aged ≥60 years, 2678 (12.2%) ≥65 years and 1045 (4.8%) ≥70 years. Data from the hospital registry revealed that 30% of adult registrations were ≥60 years. There was a significant increase in the proportion of older patients enrolled in clinical trials from 2003 (8%) to 2019 (22%) compared with their proportion in the hospital registry (stable at 28%-29%); p<0.001.
Conclusion: There is a gap between the proportion of older Indian adults with cancer in the hospital registry and those enrolled in interventional clinical trials, however, this gap has shrunk over time. Various factors that limit the recruitment of this vulnerable cohort like age-specific eligibility criteria are immediately actionable to make clinical trials more inclusive.
Keywords: Medical oncology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Centralized Circular Information System [14-Jun-2024]. https://documents.doptcirculars.nic.in/D2/D02est/25012_8_98-Estt-A.pdf Available. Accessed.
-
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare [14-Jun-2024]. https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/detailed%20breif%20of%20NP... Available. Accessed.
-
- eNPS [14-Jun-2024]. https://enps.nsdl.com/eNPS/NationalPensionSystem.html Available. Accessed.
-
- Bhagwasia M, Rao AR, Banerjee J, et al. Defining anthropometric thresholds (mid-arm circumference and calf circumference) in older adults residing in the community: a cross-sectional analysis using data from the population representative longitudinal aging study in India (LASI DAD) BMJ Open. 2023;13:e077530. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077530. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
