Solid Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Improved Oral Bioavailability of Relugolix: Preparation and Evaluation
- PMID: 39886543
- PMCID: PMC11780666
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S497099
Solid Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Improved Oral Bioavailability of Relugolix: Preparation and Evaluation
Abstract
Purpose: To improve the oral absorption of relugolix (RLGL), which has low oral bioavailability due to its low solubility and being a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). A solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of relugolix (RLGL-S-SMEDDS) was prepared and evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
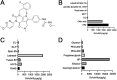
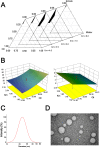
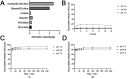
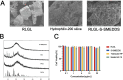
Methods: The composition of the solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SMEDDS) was selected by solubility study and pseudo-ternary phase diagram, and further optimized by Design-Expert optimization design. The optimized RLGL-S-SMEDDS were evaluated in terms of particle size, zeta potential, morphology analysis, thermodynamic stability, drug release, flow properties, transporter pathways in Caco-2 cells, the influence of excipients on the intestinal transporters, transport within Caco-2 cell monolayers and transport in lymphocyte. In vivo pharmacokinetic study and toxicological study were also conducted.
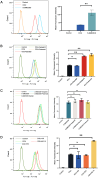
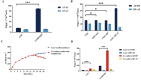
Results: The optimum formulation for self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) consists of Ethyl Oleate (26% of the weight), Solutol HS15 (49% of the weight), Transcutol HP (25% of the weight) and loaded relugolix (4.8 mg/g). The S-SMEDDS was then formed by adsorbing 2.4 g of SMEDDS onto 1 g of hydrophilic-200 silica. In phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (pH 6.8) release medium containing 1% tween 80, the vitro release studies showed 86% cumulative drug release for RLGL-S-SMEDDS and 3.6% cumulative drug release for RLGL suspensions. In vitro cellular uptake experiments revealed that the uptake of RLGL-S-SMEDDS by Caco-2 cells was three times higher than that of free RLGL, and that S-SMEDDS can enhance the drug absorption through lymphatic absorption and inhibition of intestinal transporter. In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation demonstrated that the oral bioavailability of RLGL-S-SMEDDS was 1.9 times higher than that of RLGL-suspensions. There was no apparent cardiac, hepatic, splenic, pulmonary or renal toxicity on the surface discovered by pathological analysis after oral administration.
Conclusion: It is evident that S-SMEDDS may be a safe and effective method to improve oral absorption of drugs with low oral bioavailability.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; microemulsion; oral bioavailability; relugolix; solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SMEDDS).
© 2025 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of Sophoraflavanone G: Prescription optimization and pharmacokinetic evaluation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019 Aug 1;136:104953. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31175944
-
Improving The Oral Absorption Of Nintedanib By A Self-Microemulsion Drug Delivery System: Preparation And In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Nov 6;14:8739-8751. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S224044. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31806968 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Drug Delivery Approach via Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Asenapine Maleate: Optimization, Characterization, Cell Uptake, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 Jan 7;20(2):44. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-1212-z. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 30617712
-
Self microemulsifying drug delivery system of lurasidone hydrochloride for enhanced oral bioavailability by lymphatic targeting: In vitro, Caco-2 cell line and in vivo evaluation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019 Oct 1;138:105027. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105027. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31377133
-
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS)--challenges and road ahead.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):675-90. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.896058. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24670091 Review.
References
-
- Osuga Y, Seki Y, Tanimoto M, et al. Relugolix, an oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonist, reduces endometriosis-associated pain in a dose-response manner: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Fertil Steril. 2021;115(2):397–405. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.07.055 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

