Knowledge, Attitudes, Perceptions, and Practices Related to Artificial Intelligence in Radiology Among Indian Radiologists and Residents: A Multicenter Nationwide Study
- PMID: 39886734
- PMCID: PMC11781242
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.76667
Knowledge, Attitudes, Perceptions, and Practices Related to Artificial Intelligence in Radiology Among Indian Radiologists and Residents: A Multicenter Nationwide Study
Abstract
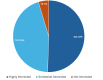
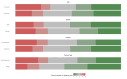
Background Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing medical science, with significant implications for radiology. Understanding the knowledge, attitudes, perspectives, and practices of medical professionals and residents related to AI's role in radiology is crucial for effective integration. Methods A cross-sectional survey was conducted among members of the Indian Radiology & Imaging Association (IRIA), targeting practicing radiologists and residents across academic and non-academic institutions. An anonymous, self-administered online questionnaire assessed AI awareness, usage, and perceptions, distributed via medical networks and social media. Descriptive statistics and chi-square tests were used to analyze the data, with statistical analysis performed using R version 4.2.2 (R Core Team (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/). Results The survey gathered responses from 404 participants nationwide. A significant portion (95.3%) demonstrated a keen interest in expanding their knowledge of AI and recommended implementing educational initiatives that increase exposure to AI. Considerable concern about losing their jobs to AI was observed only in 27.9% of respondents. More than two-thirds (86.6%) of the respondents opined that the AI curriculum should be taught during residency and 75.7% are interested in collaborating with software developers to learn and start AI at their workplace. Conclusion The survey highlights the growing importance of AI in radiology, underscoring the need for enhanced AI education and training in medical curricula.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; knowledge; physicians; radiology; residents.
Copyright © 2024, Goyal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee, Sri Aurbindo Institute of Medical Sciences, Indore issued approval SAIMS/IEC/54. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Bohr A, Memarzadeh K. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc.; 2020. The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications; pp. 25–60.
-
- Transparency of artificial intelligence in healthcare: insights from professionals in computing and healthcare worldwide. Bernal J, Mazo C. Appl Sci. 2022;12:10228.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources