Evaluation of co‑inhibition of ErbB family kinases and PI3K for HPV‑negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39886949
- PMCID: PMC11800064
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2025.8871
Evaluation of co‑inhibition of ErbB family kinases and PI3K for HPV‑negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
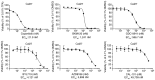
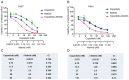
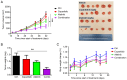
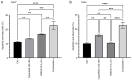
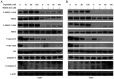
The ErbB/HER family of protein‑tyrosine kinases and PI3K represent crucial targets in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). A combination therapy of afatinib (ErbB inhibitor) and copanlisib (PI3K inhibitor), both Food and Drug Administration‑approved kinase inhibitors, can suppress the growth of human papillomavirus (HPV)‑positive HNSCC. The current study further evaluated the efficacy and clinical potential of this combination therapy for the treatment of HPV‑negative HNSCC in vitro and in vivo. Sulforhodamine B cell viability assay and Annexin V/propidium iodide staining demonstrated that this combination treatment markedly enhanced inhibition of cell viability and reduced cell survival when compared with treatment with either inhibitor alone in two HPV‑negative HNSCC cell lines. Notably, this combination also led to significant inhibition of xenograft tumor growth in mice, without any apparent effects on body weight. Western blot analysis found that copanlisib alone effectively blocked PI3K/Akt signaling but caused upregulation of HER2 and HER3 phosphorylation, as reported in other types of cancer. However, the combination of copanlisib and afatinib completely blocked phosphorylation of the ErbB family (including HER3) and Akt, while also increasing apoptosis. In conclusion, these results suggested that co‑targeting the ErbB family kinases and PI3K using a combination treatment of afatinib and copanlisib may have clinical potential for patients with HPV‑negative HNSCC.
Keywords: ErbB inhibitor; PI3K inhibitors; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hashibe M, Boffetta P, Zaridze D, Shangina O, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Mates D, Fabiánová E, Rudnai P, Brennan P. Contribution of tobacco and alcohol to the high rates of squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottis and glottis in Central Europe. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;165:814–820. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwk066. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hashibe M, Brennan P, Benhamou S, Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, Dal Maso LD, Daudt AW, Fabianova E, Fernandez L, et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:777–789. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk179. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaryouh H, De Pauw I, Baysal H, Peeters M, Vermorken JB, Lardon F, Wouters A. Recent insights in the PI3K/Akt pathway as a promising therapeutic target in combination with EGFR-targeting agents to treat head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med Res Rev. 2022;42:112–155. doi: 10.1002/med.21806. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

