mRNA vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IFN-γ and IL-2 T-cell responses are predictive of serological neutralization and are transiently enhanced by pre-existing cross-reactive immunity
- PMID: 39887249
- PMCID: PMC11915849
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01685-24
mRNA vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IFN-γ and IL-2 T-cell responses are predictive of serological neutralization and are transiently enhanced by pre-existing cross-reactive immunity
Abstract
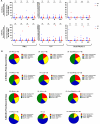
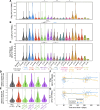
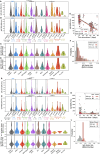
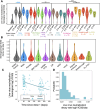
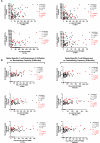
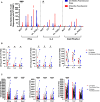
The contributions of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-specific T cells to vaccine efficacy and durability are unclear. We investigated relationships between mRNA vaccine-induced spike-specific interferon- gamma (IFN-γ) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) T-cell responses and neutralizing antibody development in long-term care home staff doubly vaccinated with BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273. The impacts of pre-existing cross-reactive T-cell immunity on cellular and humoral responses to vaccination were additionally assessed. Mathematical modeling of the kinetics of spike-specific IFN-γ and IL-2 T-cell responses over 6 months post-second dose was bifurcated into recipients who exhibited gradual increases with doubling times of 155 and 167 days or decreases with half-lives of 165 and 132 days, respectively. Differences in kinetics did not correlate with clinical phenotypes. Serological anti-spike IgG, anti-receptor binding domain (RBD) IgG, anti-spike IgA, and anti-RBD IgA antibody levels otherwise decayed in all participants with half-lives of 63, 57, 79, and 46 days, respectively, alongside waning neutralizing capacity (t1/2 = 408 days). Spike-specific T-cell responses induced at 2-6 weeks positively correlated with live viral neutralization at 6 months post-second dose, especially in hybrid immune individuals. Participants with pre-existing cross-reactive T-cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2 exhibited greater spike-specific T-cell responses, reduced anti-RBD IgA antibody levels, and a trending increase in neutralization at 2-6 weeks post-second dose. Non-spike-specific T-cells predominantly targeted SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein at 6 months post-second dose in cross-reactive participants. mRNA vaccination was lastly shown to induce off-target T-cell responses against unrelated antigens. In summary, vaccine-induced spike-specific T-cell immunity appeared to influence serological neutralizing capacity, with only a modest effect induced by pre-existing cross-reactivity.
Importance: Our findings provide valuable insights into the potential contributions of mRNA vaccine-induced spike-specific T-cell responses to the durability of neutralizing antibody levels in both uninfected and hybrid immune recipients. Our study additionally sheds light on the precise impacts of pre-existing cross-reactive T-cell immunity to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 on the magnitude and kinetics of cellular and humoral responses to vaccination. Accordingly, our data will help optimize the development of next-generation T cell-based coronavirus vaccines and vaccine regimens to maximize efficacy and durability.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; T-cell immunity; cross-reactivity; humoral immunity; hybrid immunity; mRNA vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Murphy K, Weaver C, Berg L. 2022. Janeway’s Immunobiology. 10th ed. W. Norton & Company, Inc, New York.
-
- Tarke A, Potesta M, Varchetta S, Fenoglio D, Iannetta M, Sarmati L, Mele D, Dentone C, Bassetti M, Montesano C, Mondelli MU, Filaci G, Grifoni A, Sette A. 2022. Early and polyantigenic CD4 T cell responses correlate with mild disease in acute COVID-19 donors. Int J Mol Sci 23:7155. doi:10.3390/ijms23137155 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nelson RW, Chen Y, Venezia OL, Majerus RM, Shin DS, Carrington MN, Yu XG, Wesemann DR, Moon JJ, Luster AD, MGH COVID-19 Collection & Processing Team . 2022. SARS-CoV-2 epitope-specific CD4+ memory T cell responses across COVID-19 disease severity and antibody durability. Sci Immunol 7:eabl9464. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9464 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rydyznski Moderbacher C, Ramirez SI, Dan JM, Grifoni A, Hastie KM, Weiskopf D, Belanger S, Abbott RK, Kim C, Choi J, Kato Y, Crotty EG, Kim C, Rawlings SA, Mateus J, Tse LPV, Frazier A, Baric R, Peters B, Greenbaum J, Ollmann Saphire E, Smith DM, Sette A, Crotty S. 2020. Antigen-specific adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in acute COVID-19 and associations with age and disease severity. Cell 183:996–1012. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.038 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

