Plasma proteomic characterization of motoric cognitive risk and mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 39887533
- PMCID: PMC11848158
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14429
Plasma proteomic characterization of motoric cognitive risk and mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Introduction: Motoric cognitive risk (MCR) is a pre-dementia syndrome characterized by mobility and cognitive dysfunction. This study conducted a proteome-wide study of MCR and compared the proteomic signatures of MCR to that of mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
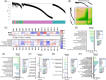
Methods: Participants were classified as MCR using a memory questionnaire and 4-meter walk. We measured 4877 plasma proteins collected during late-life and midlife. Multivariable logistic regression related each protein to late-life MCR/MCI. MCR-associated proteins were replicated internally at midlife and in an external cohort.
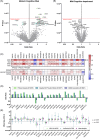
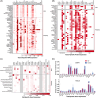
Results: Proteome-wide analysis (n = 4076) identified 25 MCR-associated proteins. Eight of these proteins remained associated with late-life MCR when measured during midlife. Two proteins (SVEP1 and TAGLN) were externally replicated. Compared to MCI, MCR had a distinct and much stronger proteomic signature enriched for cardiometabolic and immune pathways.
Discussion: Our findings highlight the divergent biology underlying two pre-dementia syndromes. Metabolic and immune dysfunction may be a primary driver of MCR.
Highlights: MCR is defined by concurrent cognitive and gait dysfunction. MCR protein biomarkers have key roles in cardiometabolic and vascular function. MCR biomarkers are also associated with cerebrovascular disease and dementia. MCR and MCI demonstrate overlapping but divergent proteomic signatures.
Keywords: dementia; mild cognitive impairment; motoric cognitive risk; pre‐dementia syndrome; proteomic.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C. (Josef Coresh) is a scientific advisor with personal fees to SomaLogic and Healthy.io. Proteomic assays in ARIC were conducted free of charge as part of a data exchange agreement with Soma Logic. The remaining authors declare no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting information.
Figures



References
-
- Montero‐Odasso M, Speechley M, Muir‐Hunter SW, et al. Motor and cognitive trajectories before dementia: results from gait and brain study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66(9):1676‐1683. - PubMed
-
- Chhetri JK, Chan P, Vellas B, Cesari M. Motoric cognitive risk syndrome: predictor of dementia and age‐related negative outcomes. Front Med. 2017;4:166. Accessed August 27, 2020. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2017.00166/full - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL096902/ARIC Neurocognitive Study
- 75N92022D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92022D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NHLBI
- R01 AG057909/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- TL1TR003100/Clinical and Translational Science
- 75N92022D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH
- U01AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
- U01HL096814/ARIC Neurocognitive Study
- TL1 TR003100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- NINDS
- R01 AG061155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL096917/ARIC Neurocognitive Study
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Intramural Research Program
- U01HL096812/ARIC Neurocognitive Study
- U01 HL096814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 523737608 (SCHL 2292/2-1)/German Research Foundation
- R01 AG057548/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92022D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI153559/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92022D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL096899/ARIC Neurocognitive Study
- R01AG057909/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute on Aging Intramural Research Program
- NIDCD
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

