Efficient Spin-Light-Emitting Diodes With Tunable Red to Near-Infrared Emission at Room Temperature
- PMID: 39887568
- PMCID: PMC11899487
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413669
Efficient Spin-Light-Emitting Diodes With Tunable Red to Near-Infrared Emission at Room Temperature
Abstract
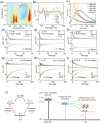
Spin light-emitting diodes (spin-LEDs) are important for spin-based electronic circuits as they convert the carrier spin information to optical polarization. Recently, chiral-induced spin selectivity (CISS) has emerged as a new paradigm to enable spin-LED as it does not require any magnetic components and operates at room temperature. However, CISS-enabled spin-LED with tunable wavelengths ranging from red to near-infrared (NIR) has yet to be demonstrated. Here, chiral quasi-2D perovskites are developed to fabricate efficient spin-LEDs with tunable wavelengths from red to NIR region by tuning the halide composition. The optimized chiral perovskite films exhibit efficient circularly polarized luminescence from 675 to 788 nm, with a photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) exceeding 86% and a dissymmetry factor (glum) ranging from 8.5 × 10-3 to 2.6 × 10-2. More importantly, direct circularly polarized electroluminescence (CPEL) is achieved at room temperature in spin-LEDs. This work demonstrated efficient red and NIR spin-LEDs with the highest external quantum efficiency (EQE) reaching 12.4% and the electroluminescence (EL) dissymmetry factors (gEL) ranging from 3.7 × 10-3 to 1.48 × 10-2 at room temperature. The composition-dependent CPEL performance is further attributed to the prolonged spin lifetime as revealed by ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy.
Keywords: chiral perovskite; circularly polarized electroluminescence; red and NIR‐LED; spin funneling; spin‐LED.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cho H., Jeong S. H., Park M. H., Y. H., Kim C. W., Lee C. L., Heo J. H., Sadhanala A., Myoung N., Yoo S., Im S. H., Friend R. H., Lee T. W., Nature 2015, 350, 6265. - PubMed
-
- Tan Z. K., Moghaddam R. S., Lai M. L., Docampo P., Higler R., Deschler F., Price M., Sadhanala A., Pazos L. M., Credgington D., Hanusch F., Bein T., Snaith H. J., Friend R. H., Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 687. - PubMed
-
- Quan L. N., Rand B. P., Friend R. H., Mhaisalkar S. G., Lee T. W., Sargent E. H., Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7444. - PubMed
-
- Liu X. K., Xu W., Bai S., Jin Y., Wang J., Friend R. H., Gao F., Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 10. - PubMed
-
- Gong S., Qu G., Qiao Y., Wen Y., Huang Y., Cai S., Zhang L., Jiang K., Liu S., Lin M., Beard M. C., Xu Z.‐X., Chen X., Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 5080.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

