Outcomes and treatment patterns for stage I human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, 2010-2019
- PMID: 39887682
- PMCID: PMC11780567
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.35729
Outcomes and treatment patterns for stage I human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, 2010-2019
Abstract
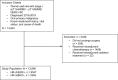
Background: The risk of recurrence in patients with small, lymph node-negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancers untreated with adjuvant chemotherapy/HER2-directed therapy is uncertain. To investigate this, the authors conducted a retrospective, population-based study of chemotherapy use and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) among patients with stage IA HER2-positive breast cancer.
Methods: The authors analyzed Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data from patients diagnosed with stage IA HER2-positive breast cancer from 2010 to 2019. They examined the frequency of chemotherapy use by tumor size and hormone receptor (HR) status and applied multivariate logistic regression to assess the factors associated with receipt of chemotherapy. BCSS was evaluated and performed multivariable Cox regression was performed to evaluate the association between chemotherapy receipt and BCSS.
Results: Among 12,896 patients, 74.0% had HR-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer, and 26.0% had HR-negative/HER2-positive breast cancer. Adjuvant chemotherapy was received by to 58.9% of patients, with lower utilization for those who were older, Hispanic or Asian/Pacific Islander, separated/divorced/widowed, or had a lower median household income. The median follow-up was 46 months. Among the patients who had pathologic T1 (pT1) microscopic, pT1a, or pT1b tumors, the 5-year BCSS rate was 97.6%-99.6% in those who had no evidence of chemotherapy receipt in the medical record versus 98.4%-100.0% in those who did receive chemotherapy. Among patients who had pT1c tumors and had no evidence of chemotherapy receipt, the 5-year BCSS rate was 92.1% for those with HR-negative/HER2-positive breast cancer and 96.0% for those with HR-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer. Patients who had pT1c tumors and received chemotherapy had a 5-year BCSS rate of 96.7% in those with HR-negative/HER2-positive breast cancer and 98.7% in those with HR-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer.
Conclusions: In this large, population-based study of patients with stage IA HER2-positive breast cancer, patients who had tumors ≤1 cm had excellent outcomes with or without chemotherapy. Patients with pT1c tumors had a greater increase in BCSS with the receipt chemotherapy.
Keywords: breast cancer‐specific survival; chemotherapy; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)‐positive; invasive disease‐free survival; Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER).
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Adrienne G. Waks reports institutional research funding from, Genentech, Gilead, Sciences, Merck, and Macrogenics; and personal/consulting fees from AMBRX and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Paolo Tarantino reports grants/contracts from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly & Company, and Gilead Sciences; personal/consulting fees from AstraZeneca, AstraZeneca UK Limited, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Hengrui Therapeutics, and Novartis; and support for other professional activities from AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Daiichi Sankyo, and F. Hoffmann‐La Roche outside the submitted work. Rachael A. Freedman reports institutional funding from Puma Biotechnology outside the submitted work. Nancy U. Lin reports institutional research support from Genentech (and Zion Pharmaceutical as part of Genentech), Pfizer, Merck, Seattle Genetics (now Pfizer), Olema Pharmaceuticals, and AstraZeneca; personal/consulting fees from Affinia Therapeutics, Aleta Biopharma, Puma, Seattle Genetics, Daiichi‐Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Olema Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Biotech Inc., Blueprint Medicines, Stemline Therapeutics/Menarini, Artera Inc., Eisai Inc., and Voyager Therapeutics; royalties from UpToDate (book); and travel support from Olema Pharmaceuticals and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Sara M. Tolaney reports research funding from Genentech/Roche, Merck, Exelixis, Pfizer, Lilly, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, AstraZeneca, Gilead, NanoString Technologies, Seattle Genetics, Noncopper, Daiichi‐Sankyo, and Menarini/Stemline; personal/consulting fees from Novartis, Pfizer (SeaGen), Merck, Eli Lilly & Company, AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Eisai, Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb, CytomX Therapeutics, Daiichi‐Sankyo, Gilead, ZymeWorks, Zentalis, Blueprint Medicines, Reveal Genomics, Sumitovant Biopharma, Umoja Biopharma, Artios Pharma, Menarini/Stemline, Aadi Bio, Bayer, Incyte Corp, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Natera, Tango Therapeutics, Systimmune, eFFECTOR, Hengrui USA, Cullinan Oncology, Circle Pharma, Arvinas, BioNTech, Johnson & Johnson/Ambrx, Launch Therapeutics, Zuellig Pharma, and Bicycle Therapeutics; and travel support from Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Gilead, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Arvinas outside the submitted work. Jose Pablo Leone reports research funding from Kazia Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly & Company, and SeaGen; and personal/consulting fees from Minerva Biotechnologies outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tarantino P, Tayob N, Dang CT, et al. Adjuvant trastuzumab emtansine versus paclitaxel plus trastuzumab for stage I HER2+ breast cancer: 5‐year results and correlative analyses from ATEMPT (TBCRC033) [abstract]. Cancer Res. 2023;83(5 suppl):PD18‐01. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.sabcs22-pd18-01 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCCN Guidelines, Version 3.2024. Invasive Breast Cancer. NCCN; 2024.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

