Transfer of the Oral Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Antagonist Relugolix Into Breast Milk of Healthy Lactating Women
- PMID: 39887952
- PMCID: PMC11781947
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.70067
Transfer of the Oral Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Antagonist Relugolix Into Breast Milk of Healthy Lactating Women
Abstract
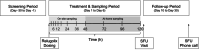
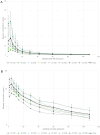
Relugolix is an oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonist that suppresses sex steroid hormones and is approved as monotherapy for prostate cancer and as a fixed-dose combination with estradiol/norethindrone for the treatment of endometriosis and uterine fibroids. The aim of this postmarketing study was to determine the pharmacokinetics and quantify the amount of relugolix excreted into breast milk of healthy lactating women. Following a single, oral dose of 40 mg relugolix, breast milk was sampled over 120 h. Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined, including the cumulative amount of relugolix excreted into breast milk to derive the total infant dose. The safety and tolerability of relugolix were also assessed. Eight healthy lactating women were enrolled and completed the study per protocol. Relugolix was safe and well tolerated based on adverse events and other safety data. It was excreted into breast milk with a median time to peak concentration (tmax) of 5.81 h and a geometric mean peak concentration (Cmax) of 15.7 ng/mL, similar to corresponding plasma data from previous clinical studies. The mean cumulative amount of relugolix excreted was 0.0051 mg over 24 h and 0.0067 mg over 120 h, corresponding to 0.0128% and 0.0167% of the maternal dose, respectively. The body weight-adjusted relative daily infant dose of approximately 0.25% suggests a 400-fold lower newborn than maternal relugolix exposure. Relevant effects of relugolix on the breastfed child appear unlikely given its limited excretion into breast milk of lactating women but cannot be fully excluded in the absence of infant safety data.
Keywords: breast milk; endometriosis; gonadotropin; lactation; pharmacokinetics; relugolix; uterine fibroids.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.‐L.C., K.Y., and M.U. are employees of Sumitomo Pharma. S.L. is a former employee of Sumitomo Pharma. D.B.B. served as the principal investigator.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart E. A., Lukes A. S., Venturella R., et al., “Relugolix Combination Therapy for Uterine Leiomyoma‐Associated Pain in the LIBERTY Randomized Trials,” Obstetrics and Gynecology 139, no. 6 (2022): 1070–1081. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration—Center for Drug Evaluation Research , “Myfembree: Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutics Review(s),” 2021, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2021/214846Orig1s000C....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

