Maladaptive Peripheral Ketogenesis in Schwann Cells Mediated by CB1R Contributes to Diabetic Neuropathy
- PMID: 39887953
- PMCID: PMC11967812
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202414547
Maladaptive Peripheral Ketogenesis in Schwann Cells Mediated by CB1R Contributes to Diabetic Neuropathy
Abstract
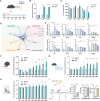
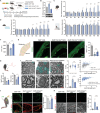
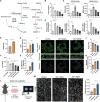
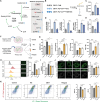
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is the most common complication of diabetes. Although studies have previously investigated metabolic disruptions in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the exact metabolic mechanisms underlying DPN remain largely unknown. Herein, a specific form of metabolic remodeling involving aberrant ketogenesis within Schwann cells (SCs) in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type I diabetes mellitus is identified. The PNS adapts poorly to such aberrant ketogenesis, resulting in disrupted energy metabolism, mitochondrial damage, and homeostatic decompensation, ultimately contributing to DPN. Additionally, the maladaptive peripheral ketogenesis is highly dependent on the cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R)-Hmgcs2 axis. Silencing CB1R reprogrammed the metabolism of SCs by blocking maladaptive ketogenesis, resulting in rebalanced energy metabolism, reduced histopathological changes, and improved neuropathic symptoms. Moreover, this metabolic reprogramming can be induced pharmacologically using JD5037, a peripheral CB1R blocker. These findings revealed a new metabolic mechanism underlying DPN, and promoted CB1R as a promising therapeutic target for DPN.
Keywords: cannabinoid type 1 receptor; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; ketogenesis; metabolic reprogramming; schwann cell.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- a) Meyer Zu Reckendorf S., Brand C., Pedro M. T., Hegler J., Schilling C. S., Lerner R., Bindila L., Antoniadis G., Knoll B., Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2123; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Selvarajah D., Kar D., Khunti K., Davies M. J., Scott A. R., Walker J., Tesfaye S., Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 938. - PubMed
-
- a) Elafros M. A., Andersen H., Bennett D. L., Savelieff M. G., Viswanathan V., Callaghan B. C., Feldman E. L., Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 922; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Pan S., Chan J. R., J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3903; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Zhang N., Ji Q., Chen Y., Wen X., Shan F., Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 193. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsuda L. A., Lolait S. J., Brownstein M. J., Young A. C., Bonner T. I., Nature 1990, 346, 561. - PubMed
-
- a) Koch M., Varela L., Kim J. G., Kim J. D., Hernandez‐Nuno F., Simonds S. E., Castorena C. M., Vianna C. R., Elmquist J. K., Morozov Y. M., Rakic P., Bechmann I., Cowley M. A., Szigeti‐Buck K., Dietrich M. O., Gao X. B., Diano S., Horvath T. L., Nature 2015, 519, 45; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Pagotto U., Marsicano G., Cota D., Lutz B., Pasquali R., Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 73; - PubMed
- c) Di Marzo V., Goparaju S. K., Wang L., Liu J., Batkai S., Jarai Z., Fezza F., Miura G. I., Palmiter R. D., Sugiura T., Kunos G., Nature 2001, 410, 822; - PubMed
- d) Hebert‐Chatelain E., Desprez T., Serrat R., Bellocchio L., Soria‐Gomez E., Busquets‐Garcia A., Pagano Zottola A. C., Delamarre A., Cannich A., Vincent P., Varilh M., Robin L. M., Terral G., Garcia‐Fernandez M. D., Colavita M., Mazier W., Drago F., Puente N., Reguero L., Elezgarai I., Dupuy J. W., Cota D., Lopez‐Rodriguez M. L., Barreda‐Gomez G., Massa F., Grandes P., Benard G., Marsicano G., Nature 2016, 539, 555. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023SCZ07/Health Scientific Research Talents Special Project of Jilin Province
- 2023SCZ01/Health Scientific Research Talents Special Project of Jilin Province
- YDZJ202301ZYTS017/Scientific and Technological Development Program of Jilin Province
- 2023C040-4/Jilin Industrial Technology Research and Development Project
- YDZJ202302CXJD060/Science and technology innovation platform construction project of Jilin Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
