Progranulin Plays a Protective Role in Pneumococcal Meningitis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis
- PMID: 39887961
- PMCID: PMC11783684
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.70140
Progranulin Plays a Protective Role in Pneumococcal Meningitis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis
Abstract
Objective: Pneumococcal meningitis is a serious infectious disease with a high mortality rate and a global presence, and survivors have different degrees of neurological sequelae as a consequence of the host response to the infection. Progranulin (PGRN) is a multifunctional autocrine growth factor that is also a major immunoregulator. We want to investigate the role for PGRN in Pneumococcal meningitis in vivo and in vitro.
Method: Mouse and cell models were established to explore the protective effect and mechanism of PGRN against pneumococcal meningitis.
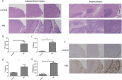
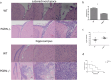
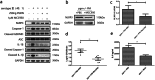
Results: Progranulin plays a protective role in pneumococcal meningitis by inhibiting pyroptosis. Pyroptosis resulted from exposure of BV-2 cells to the bacterium and this was confirmed in the in vivo model. Administration of the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 to mice prior to infection inhibited pyroptosis and protected PGRN -/- mice and BV-2 cell model from meningitis.
Conclusion: This study implicates a protective role for PGRN in pneumococcal meningitis by inhibiting pyroptosis, indicating that PGRN may have therapeutic potential.
Keywords: pneumococcal meningitis; progranulin; pyroptosis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

